-
 Home
Home
-
 News
News
Latest Educational News Stories
Daily update of all national, international news, picture stories, college / university announcements and educational events.
-
 Colleges
Colleges
Pakistan's Largest Database of Colleges and Universities
Explore Largest Directory of Private and Govt. Colleges, Universities and find best institute for your future Education.
-
 Courses
Courses
-
 Admission
Admission
-
 Lectures
Lectures
-
 Online Test
Online Test
Short Question
- 9th Class Physics Short Questions
- 9th Class Chemistry Short Questions
- 9th Class Math Short Questions
- 9th Class Biology Short Questions
- 9th Class Computer Short Questions
- 9th Class English Short Questions
- 10th Class Physics Short Question
- 10th Class Chemistry Short Question
- 10th Class Math Short Question
- 10th Class Biology Short Question
- 10th Class Computer Short Question
- 10th Class English Short Question
-
 Past Papers
Past Papers
-
 Date Sheets
Date Sheets
-
 Results
Results
Exam Results 2024
Check online Results 2024 Matric Inter BA BSc B.Com MA MSc M.Com CSS PCS MCAT ECAT of all educational boards and universities in Pakistan
-
 Study Abroad
Study Abroad
Study Abroad Programs and Opportunities for Pakistani Students
Explore free study abroad search to find programs, consultants, events to study in USA, UK, Australia, China, Malaysia and many others.
-
 Jobs
Jobs
-
 Tutors
Tutors
-
 More
More
-
 Apps
Apps
MCQ's Test For Chapter 0 "FSC Part 2 Mathematics Chapter 3 Online Test"
Try The MCQ's Test For Chapter 0 "FSC Part 2 Mathematics Chapter 3 Online Test"
-
Total Questions20
-
Time Allowed30
Question # 1
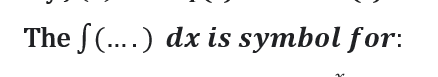
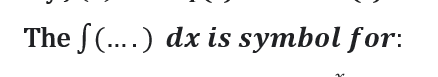
Question # 2
If the graph of f is entirely below the x-axis, then the definite integral is:
Question # 3
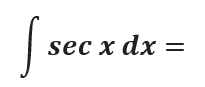
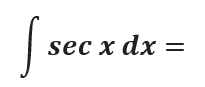
Question # 4
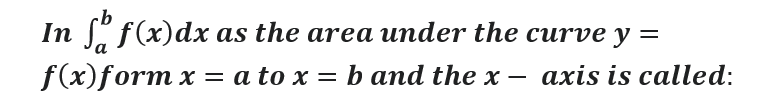
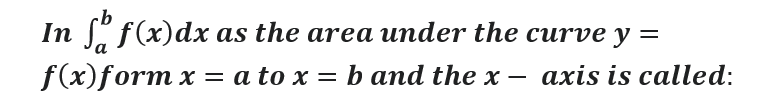
Question # 5
Area between x-axis and the curve:
Question # 6
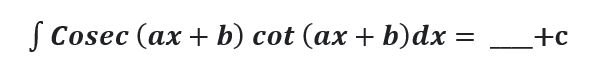
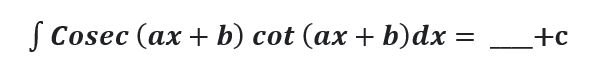
Question # 7


Question # 8
An integral of 3x2 is:
Question # 9
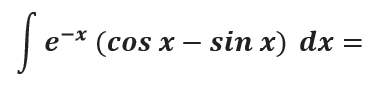
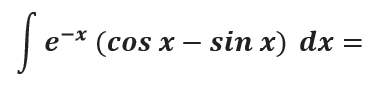
Question # 10
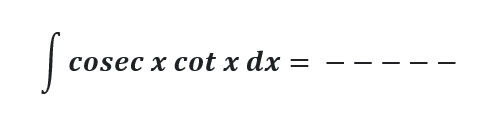
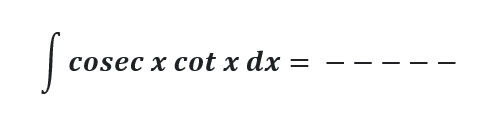
Question # 11
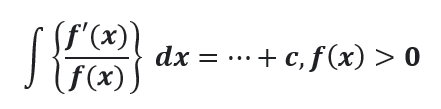
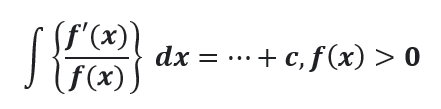
Question # 12
If the graph of f is entirely above the x-axis, then the definite integral is _______:
Question # 13


Question # 14
The term dy (or df) = f '(x) dx is called the __________ of the dependent variable y.
Question # 15
The general solution of differential equation of order n contains n arbitrary constants, which can be determined by ------------ initial value conditions.
Question # 16
If the upper limit is a constant and the lower limit is a variable, then the integral is a function of:
Question # 17
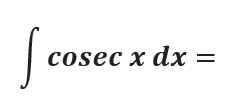
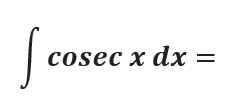
Question # 18
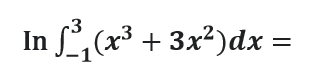
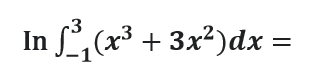
Question # 19
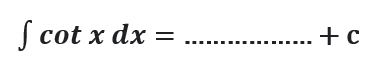
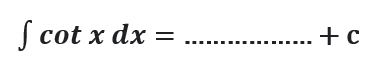
Question # 20
If y = sin x then dy =
FSC Part 2 Mathematics Chapter 3 Online Test MCQ's
Top Scorers Of Chapter 0 "FSC Part 2 Mathematics Chapter 3 Online Test" MCQ`s Test
-
N Nayab Munawer 31 - Dec - 2024 02 Min 18 Sec 19/20 -
B Baig 01 - Nov - 2025 03 Min 34 Sec 19/20 -
S SATORU Jojo plays 05 - Nov - 2024 03 Min 44 Sec 19/20 -
A Ali Hassan 19 - Nov - 2024 25 Min 47 Sec 19/20 -
S Sanwal Gakhar 23 - Oct - 2024 02 Min 40 Sec 18/20 -
Q Qadir Chaudhary 29 - Oct - 2024 02 Min 55 Sec 17/20 -
R rabia shakeel 20 - Dec - 2024 08 Min 22 Sec 17/20 -
A Ahmed Shaaff 23 - Oct - 2024 03 Min 04 Sec 16/20 -
N noor zinger 10 - Feb - 2026 04 Min 04 Sec 16/20 -
M Meerab Fatima 24 - Oct - 2025 10 Min 19 Sec 16/20 -
A Ajlal Haider 20 - Dec - 2024 02 Min 29 Sec 15/20 -
H Hanook Masih 29 - Dec - 2024 04 Min 51 Sec 15/20 -
A Abdullah Faryad 28 - Aug - 2024 14 Min 02 Sec 15/20 -
T Talha Kayani 23 - Oct - 2024 02 Min 42 Sec 14/20 -
A Ansaf Awan 24 - Oct - 2024 03 Min 18 Sec 14/20
FSc Part II Mathematics Chapter 0 Important MCQ's
| Sr.# | Question | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |

|
A. e2x sin x + c
B. e2xcosx + c
C. -e2xsin x + c
D. -e2xcosx + c
|
| 2 | Area between x-axis and the curve: |
A. 32
D. 16
|
| 3 |

|
A. f(x)
B. ln |f(x)|
C. f'(x)
D. ln |f'(x)|
|
| 4 |

|
A. cos x + c
B. - cos x + c
C. sin x + c
D. -sin x + c
|
| 5 |

|
A. domain
B. range
C. lower limit
D. upper limit
|
| 6 |

|
|
| 7 |

|
|
| 8 |

|
A. Derivative
B. Differential
C. Integral
D. None of these
|
| 9 |

|
A. eax
B. f(x)
C. eaxf(x)
D. eax + f(x)
|
| 10 | If the upper limit is a constant and the lower limit is a variable, then the integral is a function of: |
A. x
B. y
C. lower limit
D. upper limit
|








.jpg)











