-
 Home
Home
-
 News
News
Latest Educational News Stories
Daily update of all national, international news, picture stories, college / university announcements and educational events.
-
 Colleges
Colleges
Pakistan's Largest Database of Colleges and Universities
Explore Largest Directory of Private and Govt. Colleges, Universities and find best institute for your future Education.
-
 Courses
Courses
-
 Admission
Admission
-
 Lectures
Lectures
-
 Online Test
Online Test
Short Question
- 9th Class Physics Short Questions
- 9th Class Chemistry Short Questions
- 9th Class Math Short Questions
- 9th Class Biology Short Questions
- 9th Class Computer Short Questions
- 9th Class English Short Questions
- 10th Class Physics Short Question
- 10th Class Chemistry Short Question
- 10th Class Math Short Question
- 10th Class Biology Short Question
- 10th Class Computer Short Question
- 10th Class English Short Question
-
 Past Papers
Past Papers
-
 Date Sheets
Date Sheets
-
 Results
Results
Exam Results 2024
Check online Results 2024 Matric Inter BA BSc B.Com MA MSc M.Com CSS PCS MCAT ECAT of all educational boards and universities in Pakistan
-
 Study Abroad
Study Abroad
Study Abroad Programs and Opportunities for Pakistani Students
Explore free study abroad search to find programs, consultants, events to study in USA, UK, Australia, China, Malaysia and many others.
-
 Jobs
Jobs
-
 Tutors
Tutors
-
 More
More
-
 Apps
Apps
ICS Part 2 Statistics Online
Chapter 12 Test
Start Chapter
12 Test
ICS Part 2 Statistics Chapter Wise Online
MCQ's Test
MCQ's Test For Chapter 0 "ICS Part 2 Statistics Chapter 12 Online Test"
Try The MCQ's Test For Chapter 0 "ICS Part 2 Statistics Chapter 12 Online Test"
-
Total Questions17
-
Time Allowed20
Question # 1
100(1-α)% confidence interval for population proportion of success,&=nbsp;π is
Question # 2
If mean of the sampling distribution is equal to the parameter then the estimator will be
Question # 3
If population proportion (P) is unknown, the standard error of the sample proportion (p) can be estimated by the formula
Question # 4
If (1-α) is increased, the with of a confidence interval is:
Question # 5
If the observations are paired and the number of pairs is n, then the number of degree of freedom is equal to
Question # 6
Small sample has less than
Question # 7
Statistical inference has two branches namely:
Question # 8
The following statistic are unbiased estimators:
Question # 9
Estimation is of two types:
Question # 10
Estimate is the observed value of an:
Question # 11
Types of statistical inferences are
Question # 12
The process of making estimates about the population parameter from a sample is called:
Question # 13
(1-α) is called:
Question # 14
A single value used to estimate a population value is called:
Question # 15
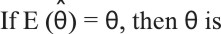
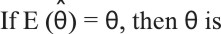
Question # 16
An estimator is ------------ if its expected value is equal to the population parameter to be estimated
Question # 17
Level of significance is denoted by
ICS Part 2 Statistics Chapter 12 Online Test MCQ's
Top Scorers Of Chapter 0 "ICS Part 2 Statistics Chapter 12 Online Test" MCQ`s Test
-
U Unknown 19 - Apr - 2024 00 Min 28 Sec 17/17 -
G GMD GUJJAR 19 - Apr - 2024 00 Min 28 Sec 17/17 -
M Muhammad Asif 22 - May - 2024 01 Min 36 Sec 17/17 -
M Muhammad Awais 19 - Apr - 2024 01 Min 45 Sec 16/17 -
N Nabeeel nabeeel 19 - Apr - 2024 01 Min 45 Sec 16/17 -
A ABBASI BEAST 18 - Apr - 2024 02 Min 15 Sec 16/17 -
K Khizer Ali 19 - Apr - 2024 02 Min 13 Sec 15/17 -
S Syed shah 16 - Nov - 2024 03 Min 38 Sec 15/17 -
Z zohaib razaq 28 - Oct - 2024 07 Min 31 Sec 15/17 -
U Usama Zaheerdar 20 - Apr - 2024 02 Min 39 Sec 14/17 -
? ????? ????? 20 - Apr - 2024 03 Min 02 Sec 14/17 -
H Hassan Peer 10 - Dec - 2023 01 Min 58 Sec 13/17 -
W Wahib Aslam 20 - Apr - 2024 02 Min 01 Sec 13/17 -
A Areeha Waheed 09 - Jul - 2024 02 Min 33 Sec 13/17 -
R rizwan gujjar 17 - Jan - 2024 02 Min 46 Sec 13/17
ICS Part II Statistics Chapter 0 Important MCQ's
| Sr.# | Question | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | If 1-α = 0.90, the value of Za/2 is: |
A. 1.645
B. 1.96
C. 2.326
D. 2.575
|
| 2 | The standard error of the estimate increased by decreasing |
A. population
B. sample size
C. errors
D. precision
|
| 3 | Confidence intervals which are often used in practice are |
A. 90%
B. 95%
C. 98%
D. all of these
|
| 4 | If (1-α) is increased, the with of a confidence interval is: |
A. Decreased
B. Increased
C. Constant
D. Same
|
| 5 | An estimator is ------------ if its expected value is equal to the population parameter to be estimated |
A. bad
B. biased
C. unbiased
D. none of these
|
| 6 | Large sample contains more than |
A. 5 values
B. 10 values
C. 20 values
D. 30 values
|
| 7 | By increasing the sample size, the precision of confidence interval is: |
A. Decreased
B. Increased
C. Constant
D. Unchanged
|
| 8 | Estimation is of two types: |
A. One sides and two sides
B. Type I and type II
C. Point estimation and interval estimation
D. Biased and unbiased
|
| 9 | A single value used to estimate a population value is called: |
A. Interval estimate
B. Point estimate
C. Confidence interval
D. Level of confidence
|
| 10 | Types of statistical inferences are |
A. one
B. two
C. three
D. four
|








.jpg)











