-
 Home
Home
-
 News
News
Latest Educational News Stories
Daily update of all national, international news, picture stories, college / university announcements and educational events.
-
 Colleges
Colleges
Pakistan's Largest Database of Colleges and Universities
Explore Largest Directory of Private and Govt. Colleges, Universities and find best institute for your future Education.
-
 Courses
Courses
-
 Admission
Admission
-
 Lectures
Lectures
-
 Online Test
Online Test
Short Question
- 9th Class Physics Short Questions
- 9th Class Chemistry Short Questions
- 9th Class Math Short Questions
- 9th Class Biology Short Questions
- 9th Class Computer Short Questions
- 9th Class English Short Questions
- 10th Class Physics Short Question
- 10th Class Chemistry Short Question
- 10th Class Math Short Question
- 10th Class Biology Short Question
- 10th Class Computer Short Question
- 10th Class English Short Question
-
 Past Papers
Past Papers
-
 Date Sheets
Date Sheets
-
 Results
Results
Exam Results 2024
Check online Results 2024 Matric Inter BA BSc B.Com MA MSc M.Com CSS PCS MCAT ECAT of all educational boards and universities in Pakistan
-
 Study Abroad
Study Abroad
Study Abroad Programs and Opportunities for Pakistani Students
Explore free study abroad search to find programs, consultants, events to study in USA, UK, Australia, China, Malaysia and many others.
-
 Jobs
Jobs
-
 Tutors
Tutors
-
 More
More
-
 Apps
Apps
General Math is a compulsory subject for 10th class art group students and it plays an important part in the overall matric result of a student. You should avail this chance of preparation because we are offering an online 10th class general math chapter 3 mcqs test. You’ll be able to solve this test online from the comfort of your home. You don’t have to pay for an expensive test session in a prestigious academy, you can login to our website and start solving these online mcqs right away. The process of attempting this online test given below on this page. If you feel that it’s still too early to take up the online mcqs test, you can prepare general math 10th class Chapter 3 mcqs from this page with help of our provided 10th class general math Chapter 3 mcqs solved PDF files.
How to Attempt Mcqs Online Test
First of all your test will be conducted online and 10th class general math test of chapter 3 will consist of 15 multiple choice questions. Total time allowed will be 20 minutes and total marks will be 15 for the whole mcqs test. Click the “Start Chapter 3 Test", this will take you to another page. From that page you can press the “Start Test” Button and in the new tab your online test will start right away. You have to choose your answers one by one for all questions. The process is the same for solving all other 10th class general math Chapters.
MCQ's Test For Chapter 3 "Algebraic Manipulation"
Try The MCQ's Test For Chapter 3 "Algebraic Manipulation"
-
Total Questions15
-
Time Allowed20
The symbol '>' stand for:
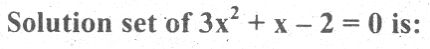
An equation that can be written in the form ax + b = 0, a ≠ 0 where a and ab are constants and x is variable is called:
Two liner algebraic expressions joined by an inequality symbol such as >,<, >,< is called:
Factor of x3 - 4x - 77 = 0 are:
for any there numbers x,y and z if x > y and y> z then:
Root which are not the solution of the original equation but they are obtained in the solution are called:
If a x b = 0 then a = 0 or b = 0 (both a and b equal to zero) is called:
The solution set of absolute equation lx - 3l = 5 is:
Any value of the variable which makes the equation a true statement is called the:
The solution set of x - 7< 5 - 2x is:
Any term of an equation may be taken to the other side with its sign changed without affection the equation is called:
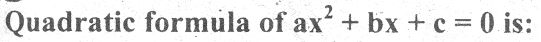
A father's age 4 times of his son's age. if the age of son is 20 year's then the age of father is:
The quadratic form of x - 5/2x= x - 4/3 is:
Prepare Complete Set Wise Chapter 3 "Algebraic Manipulation" MCQs Online With Answers
-
Set 1
15 Questions
Start
Benefits of Our Online Mcqs Test
- Self-assessment.
- Saves your time and travel cost
- More preparation in less time
- Your paper attempting speed will increase.
- You’ll better understand the summary of the Chapter.
Features of Our Online Testing System
- Your test attempting time will be recorded, you can try again to beat your own paper solving time record.
- After attempting the test you will be able to view your mistakes to improve them for the next time.
- You can share your score with your family and friends on Facebook.
- You can also challenge our result if you find that our online testing system has marked your correct answer as wrong.
Top Scorers Of Chapter 3 "Algebraic Manipulation" MCQ`s Test
-
M M Ghazanfar Talpur 10 - Feb - 2023 00 Min 51 Sec 15/15 -
A Aurnob Sarker 06 - Dec - 2023 01 Min 21 Sec 15/15 -
M Mahnoor Saif 10 - Jan - 2025 02 Min 06 Sec 15/15 -
M Masab Khan 12 - Aug - 2024 02 Min 12 Sec 15/15 -
O OP GAMING 30 - Dec - 2021 08 Min 56 Sec 14/15 -
H hamza abid 16 - Sep - 2022 10 Min 50 Sec 14/15 -
J JMK E-TUTOR 02 - Mar - 2022 00 Min 04 Sec 13/15 -
H hajra 06 - Dec - 2025 03 Min 15 Sec 13/15 -
T Tasaddaq Hussain 17 - Sep - 2024 06 Min 38 Sec 13/15 -
S Shaheen MEHBOOB 24 - Mar - 2024 01 Min 24 Sec 12/15 -
C Cooking With Ainy Raza 19 - May - 2023 05 Min 57 Sec 12/15 -
H Hifza Naeem 13 - Mar - 2023 06 Min 17 Sec 12/15 -
M Muhammad Afzal 07 - Jun - 2022 01 Min 45 Sec 11/15 -
A ayesha iqbal 12 - Feb - 2024 15 Min 00 Sec 11/15 -
A Aatika Saeed 13 - Aug - 2024 01 Min 07 Sec 10/15
10th Class (English Medium) General Maths Chapter 3 Important MCQ's
| Sr.# | Question | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Any value of the variable which makes the equation a true statement is called the: |
A. equation
B. inequality
C. variable
D. solution
|
| 2 | for any there numbers x,y and z if x > y and y> z then: |
A. trichotomy property
B. transitive property
C. additive property
D. multiplicative property
|
| 3 | Root which are not the solution of the original equation but they are obtained in the solution are called: |
A. Real roots
B. extraneous roots
C. constants
D. variable solvents
|
| 4 | Factor of x3 - 4x - 77 = 0 are: |
A. (11, -7)
B. (11, 11)
C. (11, 7)
D. (-7, 7)
|
| 5 | The symbol '>' stand for: |
A. greater than
B. less than
C. less then or equal to
D. greater than or equal to
|
| 6 |

|
|
| 7 | The solution set of x - 7< 5 - 2x is: |
A. x > 4
B. x = 4
C. x < 4
D. x < 4
|
| 8 | The quadratic form of x - 5/2x= x - 4/3 is: |
A. 2x2 -11x + 15
B. 2x2 - 15x +11
C. 2x2 -22x + 15
D. 2x2 + 11x - 15
|
| 9 | Two liner algebraic expressions joined by an inequality symbol such as >,<, >,< is called: |
A. liner equation
B. liner inequality
C. absolute value equation
D. order relation
|
| 10 | Any term of an equation may be taken to the other side with its sign changed without affection the equation is called: |
A. factorization
B. surd
C. transposition
D. transformation
|








.jpg)









Share your comments & questions here
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!