-
 Home
Home
-
 News
News
Latest Educational News Stories
Daily update of all national, international news, picture stories, college / university announcements and educational events.
-
 Colleges
Colleges
Pakistan's Largest Database of Colleges and Universities
Explore Largest Directory of Private and Govt. Colleges, Universities and find best institute for your future Education.
-
 Courses
Courses
-
 Admission
Admission
-
 Lectures
Lectures
-
 Online Test
Online Test
Short Question
- 9th Class Physics Short Questions
- 9th Class Chemistry Short Questions
- 9th Class Math Short Questions
- 9th Class Biology Short Questions
- 9th Class Computer Short Questions
- 9th Class English Short Questions
- 10th Class Physics Short Question
- 10th Class Chemistry Short Question
- 10th Class Math Short Question
- 10th Class Biology Short Question
- 10th Class Computer Short Question
- 10th Class English Short Question
-
 Past Papers
Past Papers
-
 Date Sheets
Date Sheets
-
 Results
Results
Exam Results 2024
Check online Results 2024 Matric Inter BA BSc B.Com MA MSc M.Com CSS PCS MCAT ECAT of all educational boards and universities in Pakistan
-
 Study Abroad
Study Abroad
Study Abroad Programs and Opportunities for Pakistani Students
Explore free study abroad search to find programs, consultants, events to study in USA, UK, Australia, China, Malaysia and many others.
-
 Jobs
Jobs
-
 Tutors
Tutors
-
 More
More
-
 Apps
Apps
MCQ's Test For ECAT Chemistry Chapter 11 Reaction Kinetics
Try The MCQ's Test For ECAT Chemistry Chapter 11 Reaction Kinetics
-
Total Questions30
-
Time Allowed30
Question # 1
Homogenous catalysis is that in which catalyst and reactants are in same phase. Which one of the following reaction is a homogenous catalysis
Question # 2
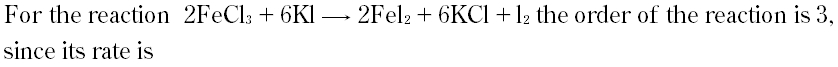
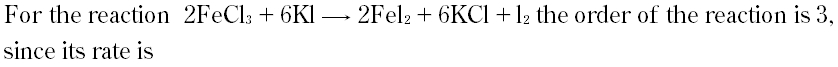
Question # 3
With the progressive of the reaction the slope of the curve between concentration of product and time
Question # 4
A pseudo uni-molecular reaction has order of reaction :
Question # 5
Complex protein molecules which catalyses the organic reactions in the living cells are called
Question # 6
In exothermic reaction decrease in potential energy of the products will result in
Question # 7
The experimental relationship between a reaction rate and the concentration of reactants is known as
Question # 8
Group l-A elements react with water fastly than the reaction of group ll-A elements because
Question # 9


Question # 10
The rate of reaction determined at a given time is called
Question # 11
Which of the following is not affected by light
Question # 12
A zero order reaction is one in which :
Question # 13
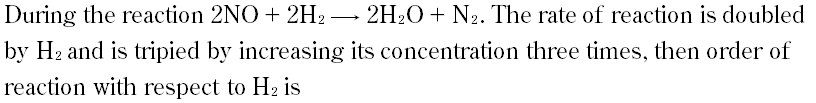
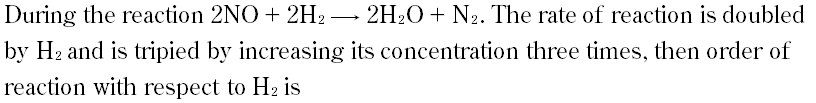
Question # 14
Which statement about Arrhenius equation is incorrect
Question # 15
When we perform the same reaction by taking two different initial concentrations of a reactant for a second order reaction then
Question # 16
The change in concentration of reactant or product per unit time is called :
Question # 17
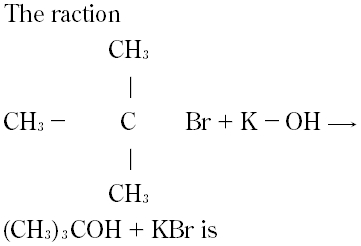

Question # 18
The example of a photo chemical reaction is photosynthesis has order of reaction :
Question # 19
In the rate equation when the concentration of reactants are unity, then rate is equal to
Question # 20
The rate of reaction :
Question # 21
The rate of reaction between two specific time intervals is called
Question # 22
Rate law of an equation is obtained :
Question # 23
With increases of 10°C temperature the rate of reactiondoubles. This increase in rate of reactionis due to :
Question # 24
Hydrolysis of ethyl-acetate (ester) has order of reaction :
Question # 25
In the expression rate = K [A]a[B]bK is
Question # 26
The addition of a catalyst to a reaction changes the
Question # 27
In an experiment the concentration of a reactant 'A' is doubled the rate increases four times. If concentration in tripled, then rate increases nint times. Thus the rate is proportional to ______ of concentration of 'A'
Question # 28
Which one of the following reaction rate is effected by the light
Question # 29
Activation energy is the difference of energy between the energy of the reactant and
Question # 30
Factor which slows down the rate of reaction is
Top Scorers Of ECAT Chemistry Chapter 11 Reaction Kinetics MCQ`s Test
-
A Abubakar basra 02 - Mar - 2024 05 Min 25 Sec 120/120 -
T Tanzeel Ur Rehman 29 - May - 2024 06 Min 39 Sec 115/120 -
M M Umer Arain 10 - Nov - 2024 00 Min 12 Sec 105/120 -
U Unaiza Usman 23 - Feb - 2024 04 Min 37 Sec 100/120 -
H Huzaifa Asim 28 - May - 2024 01 Min 53 Sec 95/120 -
G GOVT. SUFFA EDUCATION CENTER GIRLS MURIDKE 30 - May - 2024 05 Min 44 Sec 90/120 -
H Haseeb Ahmed 25 - Feb - 2024 10 Min 22 Sec 85/120 -
B Bilawal Amjad 05 - Mar - 2024 23 Min 27 Sec 80/120 -
M Maryam Fatima 19 - Mar - 2024 05 Min 45 Sec 75/120 -
M Mustaqeem 28 - Feb - 2024 11 Min 57 Sec 75/120 -
T Tamshi Sohail 22 - Apr - 2024 20 Min 02 Sec 75/120 -
S Shazi Ansari 06 - Jun - 2024 01 Min 59 Sec 70/120 -
M Muntasir Khokhar 21 - May - 2024 06 Min 02 Sec 70/120 -
U uzma majeed 11 - Mar - 2024 06 Min 47 Sec 65/120 -
Z Zubair Ayoub 07 - Mar - 2024 09 Min 18 Sec 65/120
ECAT Chemistry Chapter 11 Important MCQ's
| Sr.# | Question | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |

|
A. Rate = k[FeCl3] [Kl]2
B. Rate = k[Fe+3][Cl-1] [Kl]
C. Rate = k[Fe+3] [Cl-1][K;]
D. Rate = k[Kl]3[FeCl3]°
|
| 2 | The experimental relationship between a reaction rate and the concentration of reactants is called |
A. Order or reaction
B. Rate law
C. Activated complex
D. Molecularity
|
| 3 | The unit of rate of reaction is |
A. mole dm-3
B. mole Kg-1
C. moles dm-3sec-1
D. grams dm-3
|
| 4 | A catalyst is a substance which increase the rate of a chemical reaction, but remains unchanged at the end of reaction, nut remains unchanged at the end of reaction, because |
A. It increases the temperature
B. It increase the surface area
C. It increases the rate constant
D. It decrease the energy energy of activation
|
| 5 | When the rate of reaction is entirely independent of the conc. of reaction molecules then order of reaction is |
A. Zero
B. First
C. Second
D. Third
|
| 6 | When we perform the same reaction by taking two different initial concentrations of a reactant for a second order reaction then |
A. Reaction becomes exothermic
B. Energy of activation is different
C. Mechanism of reaction is changed
D. Half life period is changed
|
| 7 | When copper is allowed to react with HNO3, the reaction is slow in the beginning, finally becomes very fast. It is due to the formation of an auto catalyst which is |
A. Cu(NO3)2
B. CuO
C. O2
D. HNO2
|
| 8 | The reaction rate is expressed in the units of |
A. mol dm-3S-
B. mol dm-3
C. mol dm-3N-
D. dm-3S-
|
| 9 | Dilatometer method is useful for the reaction that involve : |
A. Small volume changes in solutions
B. Change in infractive indices
C. Where reactants absorb U.V, visible or infrared radiation
|
| 10 |

|
A. Small change in concentration of product
B. Small time internal
C. Co-efficient of the reactant
D. Co-efficient of the product
|








.jpg)







