-
 Home
Home
-
 News
News
Latest Educational News Stories
Daily update of all national, international news, picture stories, college / university announcements and educational events.
-
 Colleges
Colleges
Pakistan's Largest Database of Colleges and Universities
Explore Largest Directory of Private and Govt. Colleges, Universities and find best institute for your future Education.
-
 Courses
Courses
-
 Admission
Admission
-
 Lectures
Lectures
-
 Online Test
Online Test
Short Question
- 9th Class Physics Short Questions
- 9th Class Chemistry Short Questions
- 9th Class Math Short Questions
- 9th Class Biology Short Questions
- 9th Class Computer Short Questions
- 9th Class English Short Questions
- 10th Class Physics Short Question
- 10th Class Chemistry Short Question
- 10th Class Math Short Question
- 10th Class Biology Short Question
- 10th Class Computer Short Question
- 10th Class English Short Question
-
 Past Papers
Past Papers
-
 Date Sheets
Date Sheets
-
 Results
Results
Exam Results 2024
Check online Results 2024 Matric Inter BA BSc B.Com MA MSc M.Com CSS PCS MCAT ECAT of all educational boards and universities in Pakistan
-
 Study Abroad
Study Abroad
Study Abroad Programs and Opportunities for Pakistani Students
Explore free study abroad search to find programs, consultants, events to study in USA, UK, Australia, China, Malaysia and many others.
-
 Jobs
Jobs
-
 Tutors
Tutors
-
 More
More
-
 Apps
Apps
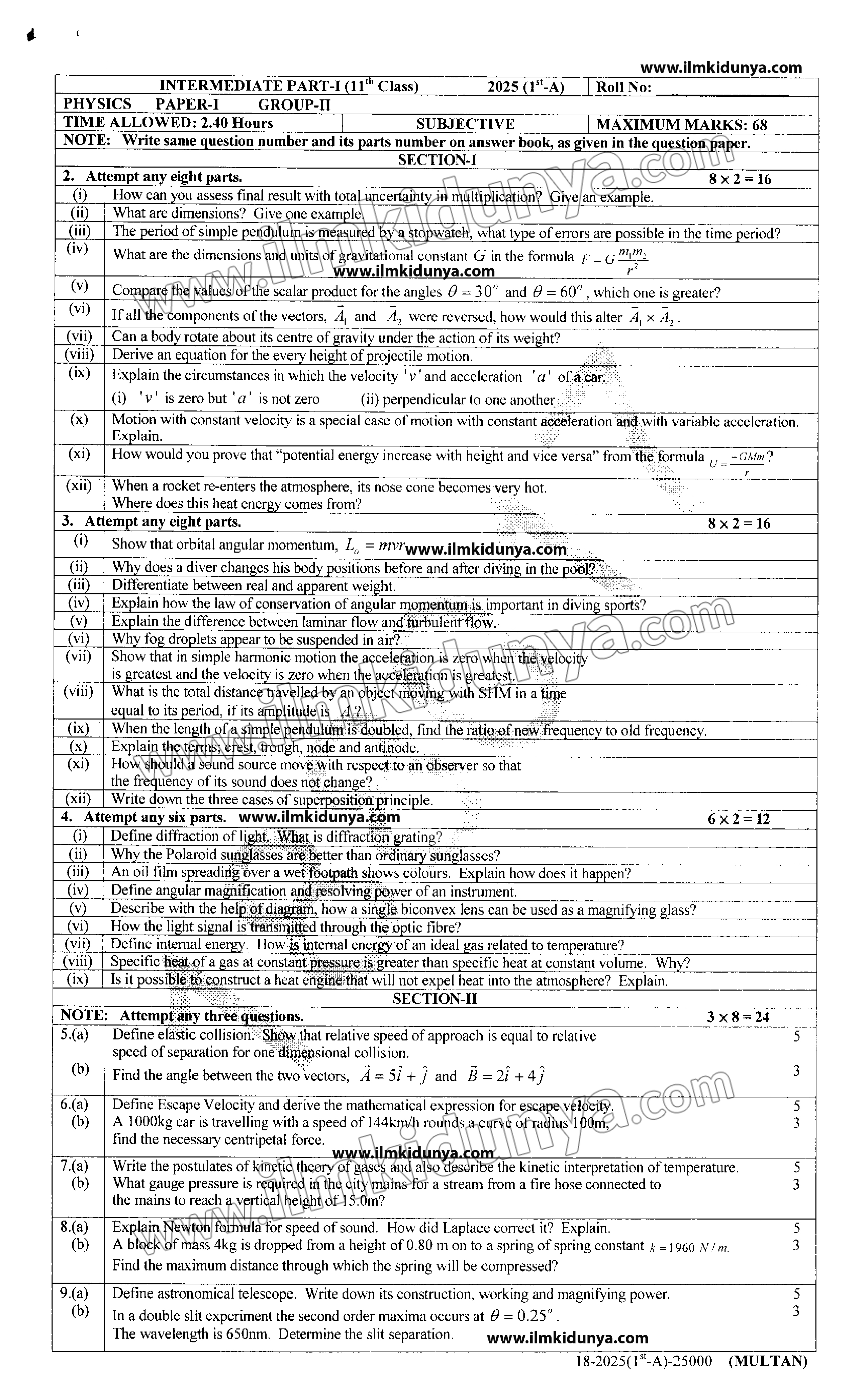
INTERMEDIATE PART-I (11th Class)
PHYSICS PAPER-I (GROUP-II)
2025 (1st-A)
TIME ALLOWED: 2:40 Hours MAXIMUM MARKS: 68
SUBJECTIVE
NOTE: Write same question number and its parts number on answer book, as given in the question paper.
SECTION–I
2. Attempt any eight parts. 8 × 2 = 16
(i) How can you assess final result with total uncertainty in multiplication? Give an example.
(ii) What are dimensions? Give one example.
(iii) The period of a simple pendulum is measured by a stopwatch; what type of errors are possible in the time period?
(iv) What are the dimensions and units of gravitational constant G in the formula F=Gm1m2r2F = G \frac{m_1 m_2}{r^2}F=Gr2m1m2?
(v) Compare the values of the scalar product for the angles θ = 30° and θ = 60°, which one is greater?
(vi) If all the components of the vectors, A₁ and A₂ , were reversed, how would this alter A₁ × A₂ ?
(vii) Can a body rotate about its centre of gravity under the action of its weight?
(viii) Derive an equation for the energy height of projectile motion.
(ix) Explain the circumstances in which the velocity v and acceleration a of a car
(i) v is zero but a is not zero (ii) perpendicular to one another.
(x) Motion with constant velocity is a special case of motion with constant acceleration and with variable acceleration. Explain.
(xi) How would you prove that “potential energy increases with height and vice versa” from the formula U=−GMmrU = -\frac{GMm}{r}U=−rGMm?
(xii) When a rocket re-enters the atmosphere, its nose cone becomes very hot. Where does this heat energy come from?
3. Attempt any eight parts. 8 × 2 = 16
(i) Show that orbital angular momentum, L=mvrL = mvrL=mvr.
(ii) Why does a diver change his body position before and after diving into the pool?
(iii) Differentiate between real and apparent weight.
(iv) Explain how the law of conservation of angular momentum is important in diving sports.
(v) Explain the difference between laminar flow and turbulent flow.
(vi) Why do fog droplets appear to be suspended in air?
(vii) Show that in simple harmonic motion the acceleration is zero when the velocity is greatest and the velocity is zero when the acceleration is greatest.
(viii) What is the total distance travelled by an object moving with SHM in a time equal to its period, if its amplitude is 4?
(ix) When the length of a simple pendulum is doubled, find the ratio of new frequency to old frequency.
(x) Explain the terms: crest, trough, node and antinode.
(xi) How should a sound source move with respect to an observer so that the frequency of its sound does not change?
(xii) Write down the three cases of superposition principle.
4. Attempt any six parts. 6 × 2 = 12
(i) Define diffraction of light. What is a diffraction grating?
(ii) Why are Polaroid sunglasses better than ordinary sunglasses?
(iii) An oil film spreading over a wet footpath shows colours. Explain how does it happen?
(iv) Define angular magnification and resolving power of an instrument.
(v) Describe with the help of a diagram how a single biconvex lens can be used as a magnifying glass.
(vi) How is the light signal transmitted through the optic fibre?
(vii) Define internal energy. How is internal energy of an ideal gas related to temperature?
(viii) Specific heat of a gas at constant pressure is greater than specific heat at constant volume. Why?
(ix) Is it possible to construct a heat engine that will not expel heat into the atmosphere? Explain.
SECTION–II
NOTE: Attempt any three questions. 3 × 8 = 24
5. (a) Define elastic collision. Show that relative speed of approach is equal to relative speed of separation for one-dimensional collision. (5)
(b) Find the angle between the two vectors, A ⃗ =5i^+j^\vec{A} = 5\hat{i} + \hat{j}A=5i^+j^ and B ⃗ =2i^+4j^\vec{B} = 2\hat{i} + 4\hat{j}B=2i^+4j^. (3)
6. (a) Define Escape Velocity and derive the mathematical expression for escape velocity. (5)
(b) A 1000 kg car is travelling with a speed of 144 km/h around a curve of radius 100 m, find the necessary centripetal force. (3)
7. (a) Write the postulates of kinetic theory of gases and also describe the kinetic interpretation of temperature. (5)
(b) What gauge pressure is required in the city mains for a stream from a fire hose connected to the mains to reach a vertical height of 15.0 m? (3)
8. (a) Explain Newton’s formula for speed of sound. How did Laplace correct it? Explain. (5)
(b) A block of mass 4 kg is dropped from a height of 0.80 m on to a spring of spring constant k=1960 N/mk = 1960 \, N/mk=1960N/m.
Find the maximum distance through which the spring will be compressed. (3)
9. (a) Define astronomical telescope. Write down its construction, working and magnifying power. (5)
(b) In a double slit experiment the second order maxima occurs at θ = 0.25°.
The wavelength is 650 nm. Determine the slit separation. (3)
Past Papers
Class Wise Past Papers
Entry Test Past Papers
Technical Education Exams Past Papers
Past Papers feedback:
If you want to share some information with other students regarding past papers, you can send your valued feedback to ilmkidunya.com







.jpg)
