Table of Content
-
Introduction
-
Understanding Social Issues in Pakistan
-
Major Social Issues in Pakistan
-
Illiteracy
-
Poverty
-
Unemployment
-
Child Labor
-
Poor Health Infrastructure
-
Foreign Debts & Unstable Economy
-
-
Current Social Issues in Pakistan
-
Climate Change and Environmental Degradation
-
Water Scarcity
-
Rising Inflation
-
Sectarianism and Extremism
-
Digital Divide
-
-
Solutions to Address Major Social Issues in Pakistan
-
The Role of Technology in Resolving Current Social Issues in Pakistan
-
Conclusion
-
FAQs
Introduction
Social Issues in Pakistan are deep-rooted and multifaceted, affecting every aspect of society. Despite some progress, challenges such as illiteracy, poverty, unemployment, child labor, and an unstable economy continue to hinder the country's growth. These major social issues in Pakistan are further exacerbated by emerging crises like climate change and inflation. Understanding these issues and implementing sustainable solutions is crucial for Pakistan's development in 2024.
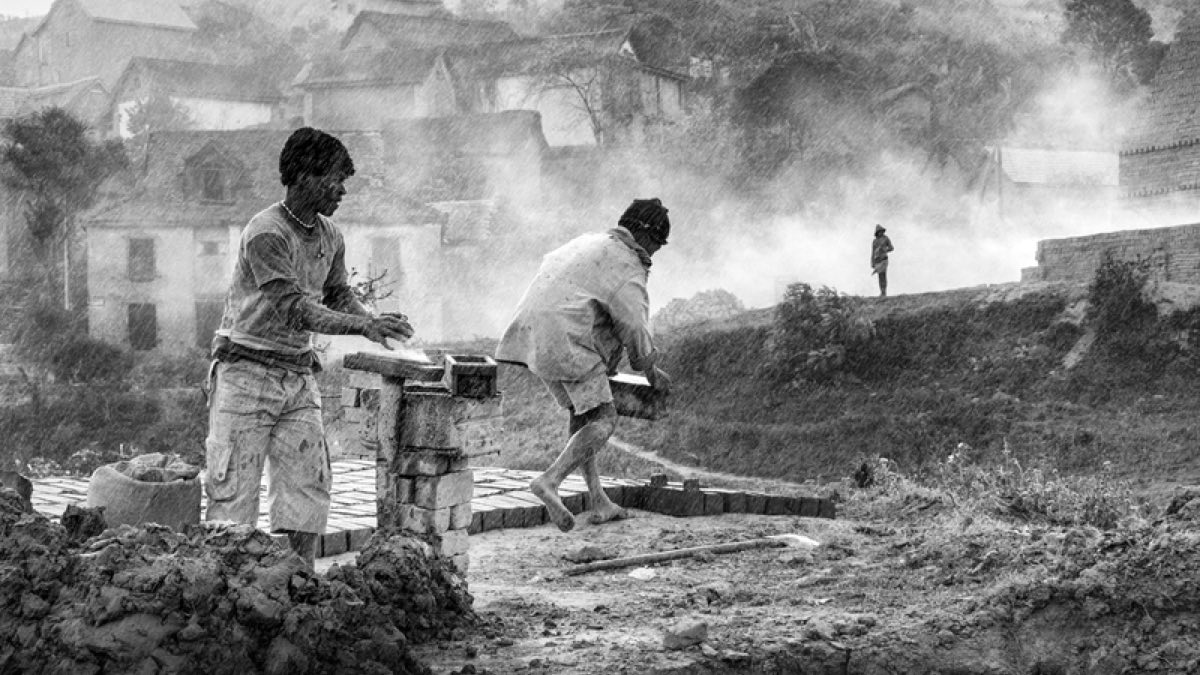

Understanding Social Issues in Pakistan
Social issues refer to the problems that negatively affect individuals and communities within a society. In Pakistan, these issues stem from systemic problems, inadequate policies, and external challenges like global economic pressures. Tackling them requires a collective effort from the government, private sector, and civil society.
Major Social Issues in Pakistan
1. Illiteracy
-
Statistics: Around 41% of Pakistan's population remains illiterate, with rural areas and women being the most affected.
-
Causes:
-
Insufficient funding for education.
-
Lack of schools and trained teachers in rural areas.
-
-
Impact:
-
Restricts access to better employment opportunities.
-
Contributes to poverty and inequality.
-
Solutions of Illiteracy in Pakistan:
Increase Education Budget to 4% of GDP:
Allocate sufficient funds to improve educational infrastructure, teacher training, and curriculum development.
Nationwide Adult Literacy Programs:
Introduce community-based programs to teach basic reading and writing skills to adults, especially in rural areas.
Improve Teacher Training:
Establish training institutes to ensure teachers are well-equipped to handle diverse classroom environments and modern teaching methods.
Build More Schools in Rural Areas:
Construct schools in underprivileged and remote regions to make education accessible to marginalized communities.
Provide Free and Compulsory Education:
Implement and enforce laws like Article 25-A of the Constitution, ensuring free education for children aged 5-16 years.
Digital Learning Initiatives:
Promote online education platforms and provide access to e-learning resources in remote areas.
Scholarships and Financial Aid Programs:
Offer financial incentives and scholarships to encourage enrollment and retention in schools, especially for girls.
Community Mobilization Campaigns:
Raise awareness about the importance of education through campaigns targeting parents and local leaders.
Early Childhood Education Programs:
Introduce preschool programs to instill a foundation for learning at an early age.
Inclusive Education Policies:
Focus on integrating marginalized groups, including girls, disabled children, and minorities, into the mainstream education system.
Public-Private Partnerships:
Encourage collaboration between the government and private sector to fund and manage schools effectively.
Mobile Schools and Libraries:
Launch mobile schools and libraries to reach nomadic communities and children in areas without permanent educational facilities.
Introduce Vocational Education:
Incorporate vocational training alongside basic education to equip students with practical skills for employment.
Promote Literacy through Media:
Leverage television, radio, and social media to disseminate educational content and motivate learning.
2. Poverty
-
Statistics: Over 37% of Pakistanis live below the poverty line, with rural areas being the hardest hit.
-
Causes:
-
Unemployment and underemployment.
-
Unequal distribution of wealth.
-
-
Impact:
-
Increased crime rates.
-
Poor health and nutrition.
-
Solutions of Poverty in Pakistan:
Promote Economic Growth:
Encourage investment in industries such as agriculture, manufacturing, and technology to create jobs and improve the standard of living.
Improve Access to Quality Education:
Education can break the cycle of poverty by equipping individuals with the skills needed for higher-paying jobs.
Expand Social Safety Nets:
Strengthen welfare programs like Benazir Income Support Program (BISP) to provide financial assistance to the poorest segments of society.
Job Creation Programs:
Introduce government-led initiatives that generate employment, such as infrastructure development and public works projects.
Microfinance and Small Business Support:
Provide low-interest loans and training to help individuals start small businesses and become self-sufficient.
Agricultural Development:
Invest in modern farming techniques, irrigation systems, and subsidies to support farmers and reduce rural poverty.
Empower Women Economically:
Encourage women's participation in the workforce through skill development programs, microloans, and equal pay policies.
Control Population Growth:
Implement family planning programs to manage population growth, which exacerbates poverty by straining resources.
Improve Healthcare Access:
Affordable and accessible healthcare reduces the financial burden of medical expenses on low-income families.
Tax Reforms:
Introduce progressive taxation policies to reduce income inequality and allocate more funds for poverty alleviation programs.
3. Unemployment
-
Statistics: Youth unemployment exceeds 10%, with a significant skills gap in the workforce.
-
Causes:
-
Economic instability.
-
Limited job opportunities in rural areas.
-
-
Impact:
-
Brain drain.
-
Increased dependency ratios.
-
Solutions of Unemployment in Pakistan:
Promote Industrial Growth:
Encourage the establishment of industries in sectors like textiles, manufacturing, and technology to generate employment opportunities.
Enhance Vocational and Technical Training:
Establish institutes offering technical and vocational training to equip workers with in-demand skills for various industries.
Encourage Entrepreneurship:
Provide funding, mentorship, and incentives to individuals who want to start their own businesses, especially in underserved areas.
Improve Agricultural Sector:
Introduce modern farming techniques, subsidies, and agro-based industries to create jobs for rural populations.
Support Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs):
Facilitate access to low-interest loans and grants for SMEs, which are a significant source of employment.
Public Works and Infrastructure Projects:
Launch government-led projects like road construction, housing, and energy infrastructure to create short-term and long-term jobs.
Revamp Education System:
Align educational curricula with market needs to ensure graduates have the skills required by employers.
Encourage Foreign Investment:
Improve ease of doing business, provide tax incentives, and ensure political stability to attract foreign investors and create jobs.
Freelancing and Remote Work Opportunities:
Promote digital skills and freelancing platforms to enable individuals to work for global clients from Pakistan.
Enhance Women's Workforce Participation:
Create policies that encourage women to join the workforce, including childcare facilities, flexible hours, and equal pay initiatives.
Expand Tourism Industry:
Develop Pakistan’s tourism potential by improving infrastructure, promoting destinations, and training locals in hospitality services.
Develop Export-Oriented Industries:
Focus on boosting exports in textiles, IT, and other sectors, which can create a significant number of jobs.
4. Child Labor
-
Statistics: Over 12.5 million children are engaged in labor in Pakistan, depriving them of education and childhood.
-
Causes:
-
Poverty and lack of education.
-
Weak enforcement of labor laws.
-
-
Impact:
-
Perpetuates cycles of poverty.
-
Affects mental and physical health of children.
-
Solutions of Child Labor in Pakistan:
Strict Enforcement of Child Labor Laws:
Ensure the implementation of laws like the Employment of Children Act, 1991, and monitor workplaces for compliance.
Provide Free and Compulsory Education:
Strengthen initiatives under Article 25-A of the Constitution to ensure every child aged 5-16 has access to free education.
Financial Assistance to Families:
Introduce welfare programs to provide financial support to families dependent on children's earnings, reducing the need for child labor.
Increase Education Infrastructure in Rural Areas:
Build more schools and provide incentives for rural children to attend instead of working.
Awareness Campaigns:
Run nationwide awareness campaigns to educate parents and communities about the harms of child labor and the benefits of education.
Corporate Accountability:
Encourage businesses to adopt ethical practices, ensuring their supply chains are free from child labor.
Ban Child Labor in Hazardous Industries:
Enforce bans on employing children in hazardous jobs, such as brick kilns, mining, and chemical factories, as per international labor standards.
Skill Development Programs for Adolescents:
Introduce vocational training programs for adolescents aged 14-18, allowing them to earn legally while developing their skills.
Promote Family Planning:
Educate families on family planning to reduce the economic burden of large families, which often leads to child labor.
Incentivize Employers:
Provide subsidies or tax benefits to employers who hire adult workers instead of children, encouraging ethical employment practices.
Engage Civil Society Organizations (CSOs):
Collaborate with NGOs and CSOs to rescue children from labor, rehabilitate them, and integrate them into the education system.
Implement Conditional Cash Transfers:
Offer financial incentives to families who ensure their children attend school instead of engaging in labor.
5. Poor Health Infrastructure
-
Statistics: Pakistan spends only 2.7% of its GDP on healthcare, ranking low in global health indices.
-
Causes:
-
Inadequate funding and resources.
-
Lack of access to healthcare in rural areas.
-
-
Impact:
-
High maternal and infant mortality rates.
-
Increased burden of communicable diseases.
-
Solutions of Poor Health Infrastructure in Pakistan:
Increase Government Spending on Healthcare:
Allocate a higher percentage of the national budget to healthcare services, aiming to raise it to at least 5% of GDP to strengthen the public health system.
Build More Healthcare Facilities in Rural Areas:
Construct new hospitals, clinics, and primary healthcare centers in underserved and rural regions to provide better access to healthcare.
Upgrade Existing Healthcare Infrastructure:
Renovate and modernize outdated hospitals and health centers to meet current healthcare demands and improve service delivery.
Recruit and Train Healthcare Professionals:
Increase the number of medical professionals, including doctors, nurses, and technicians, by offering incentives for working in rural or underdeveloped areas and by investing in medical education.
Improve the Distribution of Medical Resources:
Ensure that essential medical supplies, medicines, and equipment are distributed equally across urban and rural areas, preventing shortages.
Establish Telemedicine Services:
Develop telemedicine platforms to offer remote consultations, especially in rural areas, and reduce the burden on physical healthcare facilities.
Public-Private Partnerships (PPP):
Encourage collaboration between the government and private healthcare providers to improve infrastructure, reduce costs, and increase access to quality healthcare services.
Focus on Preventive Healthcare:
Invest in public health campaigns and awareness programs to focus on preventing diseases such as malaria, tuberculosis, and hypertension, which will reduce the overall burden on healthcare facilities.
Improve Maternal and Child Healthcare Services:
Increase the availability of maternal and child healthcare services, focusing on improving maternal mortality rates and ensuring access to immunizations and prenatal care.
Upgrade Emergency Medical Services (EMS):
Improve emergency medical services, including ambulances, emergency rooms, and trauma care units, to provide quick responses to accidents and medical emergencies.
Increase Health Insurance Coverage:
Expand and improve health insurance programs like Sehat Insaf Card, ensuring that more individuals have financial protection against high medical costs.
Improve Water and Sanitation Systems:
Invest in clean water and sanitation infrastructure to prevent waterborne diseases, which burden the healthcare system.
Develop Health Information Systems:
Create a centralized health data system to improve patient records management, enhance the efficiency of healthcare delivery, and enable better planning and resource allocation.
Encourage Medical Research and Development:
Invest in medical research to develop new treatments and technologies tailored to Pakistan's healthcare needs, and encourage innovation in medical science.
Promote Mobile Healthcare Units:
Deploy mobile health clinics to reach remote or underserved communities that lack access to fixed healthcare facilities.
6. Foreign Debts & Unstable Economy
-
Statistics: Pakistan's external debt exceeds $130 billion, with a high debt-to-GDP ratio.
-
Causes:
-
Over-reliance on foreign loans.
-
Trade deficits and low exports.
-
-
Impact:
-
Stagnant economic growth.
-
Devaluation of the Pakistani rupee.
-
Solution of Foreign Debts & Unstable Economy in Pakistan:
Debt Restructuring and Management:
Negotiate with international creditors for favorable terms, such as longer repayment periods or lower interest rates, to manage foreign debt more efficiently and reduce financial pressure.
Diversify the Economy:
Encourage the growth of non-traditional sectors, such as information technology, agriculture, and renewable energy, to reduce dependency on a few industries and enhance economic stability.
Strengthen Exports:
Focus on expanding export markets, particularly for textiles, agricultural products, and technology, by improving quality and seeking new trade agreements, which can generate foreign currency and reduce dependency on debt.
Reduce Import Dependency:
Implement policies to reduce the import of non-essential goods and promote local industries that can replace imported products, such as the local manufacturing of electronics, cars, and machinery.
Improve Tax Collection Mechanisms:
Strengthen the tax collection system by broadening the tax base, improving tax compliance, and increasing efficiency in the Federal Board of Revenue (FBR), which would increase domestic revenues and reduce reliance on loans.
Attract Foreign Direct Investment (FDI):
Create a favorable investment climate by offering tax incentives, reducing bureaucratic hurdles, and ensuring political stability to attract foreign investors, which can help reduce the reliance on loans and strengthen the economy.
Monetary and Fiscal Policies:
Implement sound monetary policies to control inflation and stabilize the currency, while ensuring fiscal discipline through budget management to avoid excessive borrowing.
Increase Remittances from Overseas Pakistanis:
Encourage Overseas Pakistanis to send remittances through official channels by offering incentives and reducing remittance transfer costs, which will help to stabilize the economy and improve foreign exchange reserves.
Strengthen Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs):
Promote SMEs by providing them with low-interest loans, tax benefits, and training. A thriving SME sector can contribute significantly to economic growth and reduce reliance on foreign debts.
Implement Structural Reforms:
Undertake comprehensive structural reforms in key sectors like energy, agriculture, and manufacturing to improve productivity, reduce inefficiencies, and increase competitiveness in global markets.
Improve the Ease of Doing Business:
Simplify regulations and reduce red tape to encourage local and foreign businesses to operate smoothly, thereby boosting economic activity and contributing to debt reduction.
Develop Human Capital:
Invest in education, skill development, and vocational training to create a skilled workforce that meets market demands and attracts investment, driving long-term economic growth.
Debt-for-Climate Programs:
Negotiate debt-for-climate swaps, where countries reduce their foreign debt burden in exchange for committing to climate change mitigation and adaptation programs, which also contribute to sustainable economic development.
Strengthen Agriculture and Rural Economy:
Introduce reforms to modernize agriculture, increase crop yields, and improve rural infrastructure, which will help boost rural incomes, reduce poverty, and stabilize the economy.
Current Social Issues in Pakistan
Climate Change and Environmental Degradation
-
Statistics: Pakistan contributes less than 1% to global emissions but ranks among the top 10 most affected countries.
-
Impact:
-
Floods and droughts.
-
Loss of agricultural productivity.
-
-
Solutions:
-
Implement disaster management plans.
-
Promote renewable energy and afforestation.
-
Water Scarcity
-
Statistics: Per capita water availability is less than 1,000 cubic meters, a critical threshold.
-
Impact:
-
Threatens agriculture, which employs 38% of the workforce.
-
Increases regional tensions over shared water resources.
-
-
Solutions:
-
Build dams and reservoirs.
-
Encourage water-saving practices.
-
Rising Inflation
-
Impact:
-
Reduces purchasing power of citizens.
-
Worsens poverty levels.
-
-
Solutions:
-
Implement price control mechanisms.
-
Promote local production to reduce reliance on imports.
-
Sectarianism and Extremism
-
Impact:
-
Threatens national unity.
-
Causes violence and instability.
-
-
Solutions:
-
Promote interfaith harmony.
-
Strengthen law enforcement against hate speech and terrorism.
-
Digital Divide
-
Impact:
-
Limits access to education and economic opportunities.
-
Worsens rural-urban disparities.
-
-
Solutions:
-
Expand internet infrastructure in remote areas.
-
Provide affordable technology for students and professionals.
-
Solutions to Address Major Social Issues in Pakistan
-
Policy Reforms: Prioritize education, healthcare, and employment in the national agenda.
-
Public-Private Partnerships: Leverage corporate investments to fund social programs.
-
Community Engagement: Involve local communities in addressing child labor, gender inequality, and environmental protection.
-
Technological Innovations: Use e-governance to improve transparency and efficiency in public services.
|
Social Issue |
Impact |
Solutions |
|
Illiteracy |
Limits economic progress |
Strengthen education infrastructure |
|
Poverty |
Increases crime rates |
Expand social welfare programs |
|
Unemployment |
Leads to brain drain |
Develop skill development centers |
|
Child Labor |
Affects childhood and education |
Enforce strict labor laws |
|
Poor Health Infrastructure |
High mortality rates |
Increase healthcare spending |
|
Foreign Debts |
Economic instability |
Diversify exports and tax reforms |
The Role of Technology in Resolving Current Social Issues in Pakistan
-
Digital Education: Bridge the literacy gap through online platforms.
-
E-Governance: Improve transparency in governance.
-
HealthTech: Expand telemedicine to provide healthcare in remote areas.
Conclusion
The social issues in Pakistan pose significant challenges, but they also present opportunities for growth and reform. Addressing major social issues in Pakistan like illiteracy, poverty, and unemployment, alongside tackling current social issues in Pakistan such as climate change and inflation, is essential for a brighter future. A united effort by all stakeholders can ensure that Pakistan overcomes these obstacles and achieves sustainable development in 2024 and beyond.
FAQs
Q1: What are the major social issues in Pakistan?
A: Illiteracy, poverty, unemployment, child labor, poor health infrastructure, and foreign debts are some major social issues in Pakistan.
Q2: How can poverty be reduced in Pakistan?
A: Poverty can be reduced through social welfare programs, rural development, and job creation initiatives.
Q3: Why is unemployment a significant issue in Pakistan?
A: Unemployment leads to economic dependency, brain drain, and increased social tensions.
Q4: What role does technology play in solving social issues?
A: Technology enhances transparency, improves education, and expands healthcare access through digital platforms.
Q5: How can foreign debts be managed effectively?
A: Diversifying exports, improving tax collection, and reducing reliance on loans are key strategies.




.gif)














Sign in
to continue to ilmkidunya.com