Some of the world’s most awe-inspiring cities are not built on land but carved directly into rock. These rock-cut cities are a testament to human ingenuity, creativity, and resilience. From ancient civilizations to modern-day wonders, these majestic cities remain some of the most fascinating destinations for history enthusiasts and travelers alike.
This article explores the history, architectural significance, cultural impact, and must-visit rock-cut cities worldwide.

The History of Rock-Cut Cities
Ancient Origins
The concept of carving cities into rock dates back thousands of years. Early civilizations sought shelter and security by carving homes, temples, and fortresses into mountains and cliffs. These structures provided protection from invaders, harsh climates, and natural disasters.
Evolution Over Centuries
Over time, rock-cut architecture evolved into intricate cityscapes with elaborate designs. Many of these cities became religious centers, trade hubs, and cultural landmarks. The use of rock-cut architecture can be seen in various ancient civilizations, including the Nabataeans, Egyptians, and Indians.
Architectural Marvels of Rock-Carved Cities
Rock-cut cities are characterized by their unique architectural elements. Below are some common features found in these cities:
|
Feature |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Monolithic Structures |
Entire buildings carved from a single rock formation. |
|
Intricate Facades |
Detailed carvings and sculptures adorn the entrances. |
|
Hidden Passageways |
Secret tunnels and pathways for security. |
|
Natural Ventilation |
Clever designs to allow air circulation. |
|
Water Management Systems |
Cisterns and aqueducts to store and distribute water. |
Famous Rock-Cut Cities Around the World
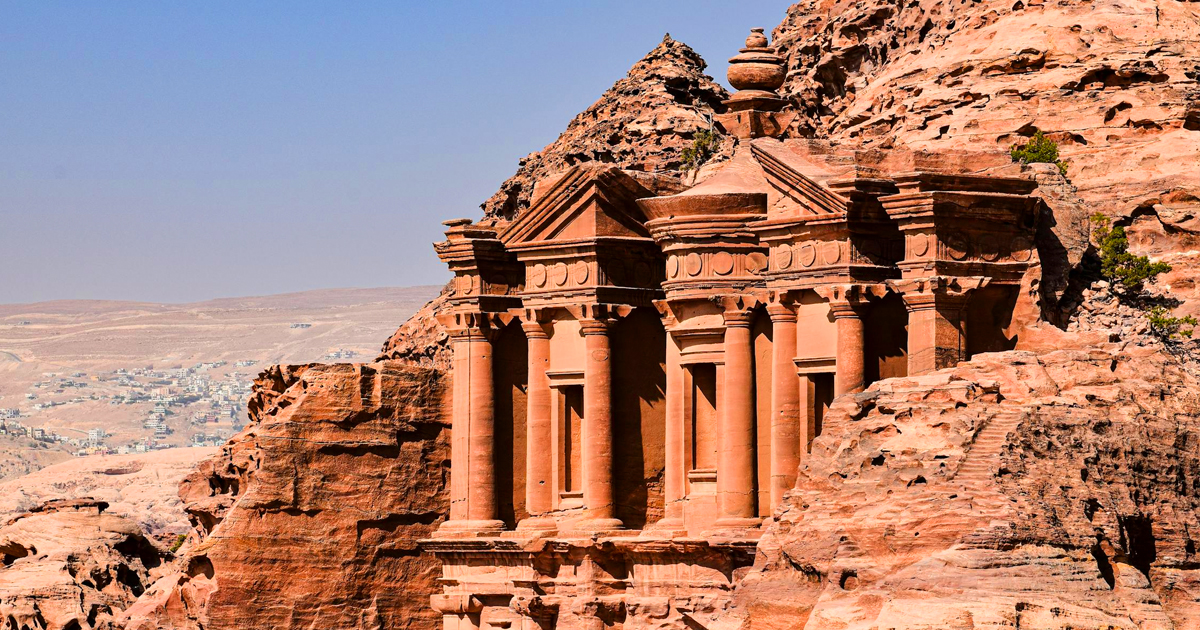
1. Petra, Jordan
Petra, the “Rose City,” is one of the most famous rock-carved cities. Built by the Nabataeans around the 4th century BC, Petra features:
-
The iconic Al-Khazneh (The Treasury)
-
The grand Monastery (Ad Deir)
-
An intricate network of tombs and temples
-
A sophisticated water conduit system
2. Ellora and Ajanta Caves, India
India is home to some of the most breathtaking rock-cut caves, including:
-
Ellora Caves: 34 rock-carved monasteries and temples spanning Hindu, Buddhist, and Jain cultures.
-
Ajanta Caves: 29 caves with stunning frescoes and sculptures depicting Buddhist teachings.
3. Meteora, Greece
Meteora is a unique rock formation housing monasteries perched atop cliffs. Features include:
-
Six active monasteries
-
Stunning panoramic views
-
Spiritual significance for Orthodox Christians
4. Lalibela, Ethiopia
Lalibela is an Ethiopian treasure known for its monolithic rock-hewn churches, including:
-
Church of Saint George (cross-shaped)
-
Underground tunnels connecting various churches
-
Religious significance as a pilgrimage site
5. Derinkuyu, Turkey
Derinkuyu is an underground city in Turkey that served as a refuge for early Christians. Highlights include:
-
Multi-level tunnels reaching depths of 60m
-
Stables, kitchens, and chapels carved into rock
-
An extensive ventilation system
Cultural Significance of Rock-Carved Cities
Rock-cut cities are not just architectural marvels but also cultural and religious centers. Many of these cities served as:
-
Religious Sanctuaries: Places of worship and pilgrimage sites
-
Trade Hubs: Locations on ancient trade routes, such as the Silk Road
-
Refuges: Safe havens from wars and invasions
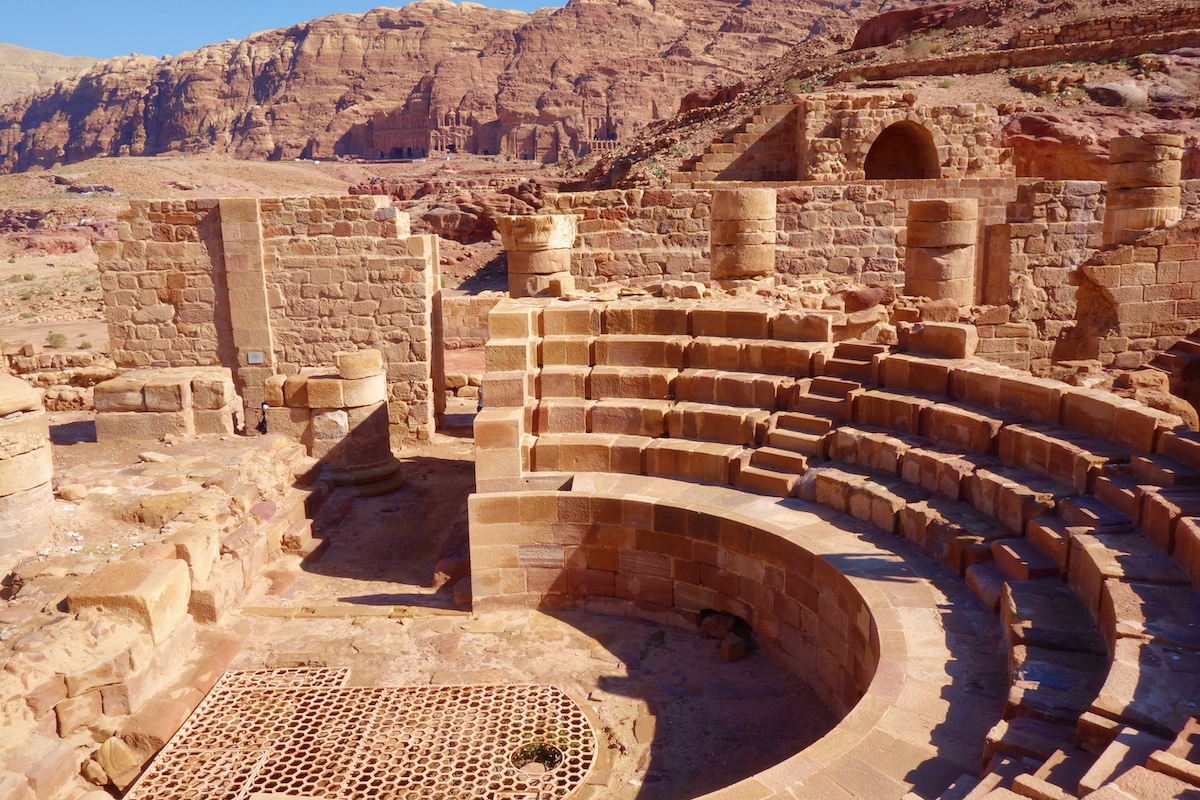

Benefits of Rock-Carved Architecture
These cities were built with purpose and efficiency, providing various advantages:
Durability
Rock-carved architecture is renowned for its exceptional durability, as structures carved directly into natural rock formations are inherently resistant to many environmental and structural challenges. Unlike freestanding buildings constructed with separate materials, rock-cut structures benefit from the strength and stability of the bedrock itself, reducing the risk of collapse or erosion. Many ancient rock-cut sites, such as Petra in Jordan or the Ajanta and Ellora Caves in India, have withstood centuries of weathering, seismic activity, and human impact. However, despite their resilience, factors like water infiltration, thermal expansion, and pollution-induced chemical reactions can gradually degrade the rock surfaces. Preservation efforts, including controlled tourism, drainage management, and conservation treatments, are crucial in maintaining the longevity of these magnificent architectural wonders.
Energy Efficiency
Rock-carved architecture exhibits remarkable energy efficiency due to the natural insulating properties of stone. Structures carved directly into rock benefit from thermal mass, which helps regulate indoor temperatures by absorbing heat during the day and releasing it at night, reducing the need for artificial heating or cooling. This makes rock-cut dwellings particularly advantageous in extreme climates, such as the desert tombs of Petra or the underground cities of Cappadocia. Additionally, since these structures require no additional construction materials like bricks or timber, they minimize resource consumption and environmental impact. Their self-supporting nature also reduces maintenance costs, making them a sustainable architectural choice that has stood the test of time.
Environmental Sustainability
Rock-carved architecture is an environmentally sustainable building method due to its minimal resource consumption and long-lasting durability. Unlike conventional construction, which requires extensive materials like wood, concrete, and steel, rock-cut structures utilize existing geological formations, reducing deforestation and carbon emissions associated with material production and transportation. Additionally, their natural insulation properties enhance energy efficiency, lowering the need for heating and cooling. Many ancient rock-cut sites, such as those in Cappadocia and Petra, have endured for centuries with minimal maintenance, demonstrating their sustainability over time. However, modern environmental threats, such as air pollution and climate change, necessitate conservation efforts to preserve these historical and eco-friendly architectural marvels.
Challenges of Preserving Rock-Carved Cities
Despite their durability, these cities face threats that require conservation efforts. Some challenges include:
|
Threat |
Impact |
|
Erosion |
Natural weathering weakens structures. |
|
Tourism Pressure |
High foot traffic damages delicate carvings. |
|
Pollution |
Acid rain and air pollution degrade rock surfaces. |
|
Urban Development |
Expansion threatens historical sites. |
Conservation Efforts
Several organizations and governments are working to preserve these historical wonders. Preservation methods include:
-
Controlled Tourism: Limiting visitor numbers to reduce impact
-
Structural Reinforcement: Using modern technology to stabilize structures
-
Documentation & Digital Archiving: Creating digital records of carvings and inscriptions
-
Legal Protection: Declaring sites as UNESCO World Heritage locations
How to Visit a Rock-Carved City Responsibly
If you plan to visit one of these breathtaking sites, consider these responsible travel tips:
-
Respect Local Guidelines: Follow conservation rules and restrictions.
-
Avoid Touching Carvings: Prevent further erosion.
-
Use Eco-Friendly Transport: Reduce environmental impact.
-
Support Local Communities: Buy from local vendors and respect cultural traditions.
Rock-carved cities are among the most fascinating architectural feats in human history. From Petra’s rose-red cliffs to Lalibela’s sacred churches, these cities showcase the brilliance of ancient civilizations. However, preserving these wonders is crucial for future generations to explore and appreciate.




.gif)














Sign in
to continue to ilmkidunya.com