Agriculture is the backbone of human civilization, providing food, raw materials, and employment to billions. Among all nations, China stands as the largest agricultural country in the world, leading in production, exports, and innovation. This article explores China’s agricultural dominance, key crops, production statistics, and its role in global food security.
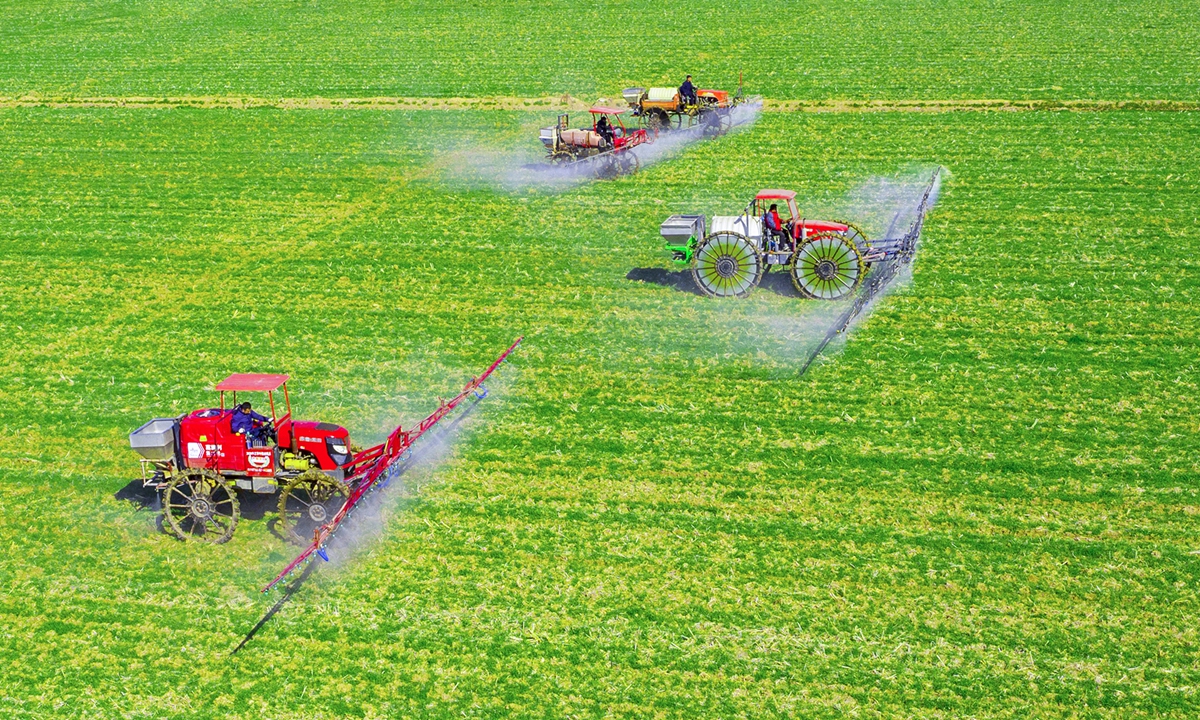

Why is China the Largest Agriculture Country?
China’s vast landmass, favorable climatic conditions, and technological advancements contribute to its agricultural supremacy. Some key factors include:
-
Extensive Farmland: With over 120 million hectares of arable land, China has one of the largest farming areas globally.
-
Diverse Climate: The country has a range of climates from temperate to tropical, allowing for year-round cultivation.
-
Large Workforce: Over 500 million people are engaged in agriculture, ensuring high productivity.
-
Government Support: Subsidies, research initiatives, and modernization efforts fuel the agricultural sector.
Additionally, China’s history and traditions are deeply intertwined with agriculture, with practices dating back thousands of years. Ancient techniques such as terrace farming and irrigation canals have been adapted into modern technological applications.
Major Agricultural Products of China
China produces a vast array of crops and livestock, dominating global markets in several categories. Some of the top agricultural products include:
-
Rice: China is the world’s largest producer, with over 200 million tons annually.
-
Wheat: Leading the world in wheat production, China produces more than 130 million tons.
-
Corn: The country ranks second in global corn production, contributing nearly 275 million tons.
-
Soybeans: China ranks fourth in soybean production, with nearly 19 million tons.
-
Potatoes: The largest producer of potatoes, with over 90 million tons annually.
-
Pork: China dominates pork production with over 55 million tons annually.
-
Vegetables: Producing over 600 million tons, China is the leading vegetable supplier.
-
Tea: The country is the top producer of tea, with an annual output exceeding 3 million tons.
-
Cotton: China leads in cotton production, generating over 6 million tons.
China’s ability to grow diverse crops ensures that it meets both domestic and international demand, contributing significantly to global food security.
Contribution to Global Agriculture
China’s agricultural dominance is not only about production but also its influence on global trade, food security, and technological advancements.
1. Global Trade Leader
China is one of the largest exporters of agricultural goods. Some key exports include:
-
Rice and wheat
-
Tea and spices
-
Fruits and vegetables
-
Livestock products (pork and poultry)
In recent years, China has expanded its agricultural exports to countries across Europe, Africa, and the Americas, strengthening its role in international food supply chains.
2. Food Security & Supply Chain Stability
China plays a crucial role in stabilizing global food markets. Its ability to meet domestic demands while exporting surplus helps maintain global food security.
With a massive population of 1.4 billion people, China must continuously innovate to sustain food supply levels. Government initiatives, including high-yield crop research and efficient distribution channels, have enhanced its food security efforts.
3. Technological Advancements in Farming
China is a leader in agri-tech, investing in:
-
Genetically modified (GM) crops for better yields
-
Smart irrigation systems to optimize water usage
-
AI and robotics for automated farming
-
Vertical farming and urban agriculture solutions
Agricultural mechanization has significantly improved efficiency, reducing reliance on manual labor while increasing productivity.
Challenges Faced by China’s Agriculture Sector
Despite its strengths, China’s agriculture sector faces multiple challenges:
1. Land Degradation & Soil Erosion
-
Overuse of fertilizers has led to soil degradation.
-
Desertification affects 27% of China’s land.
-
Continuous farming without proper crop rotation has impacted soil fertility.
2. Water Scarcity
-
Agriculture consumes 65% of China’s water resources.
-
Northern regions face severe water shortages affecting crop yields.
-
Unregulated groundwater extraction has caused water table depletion in key farming regions.
3. Climate Change
-
Rising temperatures and unpredictable rainfall patterns threaten crop production.
-
Increased frequency of droughts and floods disrupts harvest seasons.
-
Pests and diseases are becoming more resistant due to changing climate conditions.
4. Aging Farming Population
-
Young people are migrating to cities, leading to a shortage of skilled farmers.
-
Mechanization efforts are being accelerated to counter this issue.
-
Government programs are encouraging young entrepreneurs to invest in agribusinesses.

Future of Agriculture in China
1. Sustainable Agriculture Practices
To combat land degradation and water scarcity, China is adopting:
-
Organic farming techniques
-
Precision farming using AI
-
Reforestation projects to prevent desertification
-
Hydroponics and aquaponics to maximize crop production in urban areas
2. Expanding Agricultural Exports
China is focusing on increasing exports by:
-
Strengthening trade relations with Europe, Africa, and the Americas.
-
Improving product quality to meet international standards.
-
Reducing reliance on imports by enhancing self-sufficiency.
3. Boosting Domestic Production
To reduce dependence on imports, China is enhancing:
-
Self-sufficiency in grains like wheat and rice.
-
Research in hybrid crops to increase yield and resistance to pests.
-
Modern irrigation techniques to optimize water usage.
The integration of big data, AI, and blockchain into agriculture ensures transparency, efficiency, and traceability in China’s food supply chain.
By understanding China’s agricultural strengths and challenges, policymakers, farmers, and global stakeholders can better prepare for the future of global food security.
This growing industry will continue to evolve, providing innovative solutions for sustainable and efficient food production worldwide.




.gif)














Sign in
to continue to ilmkidunya.com