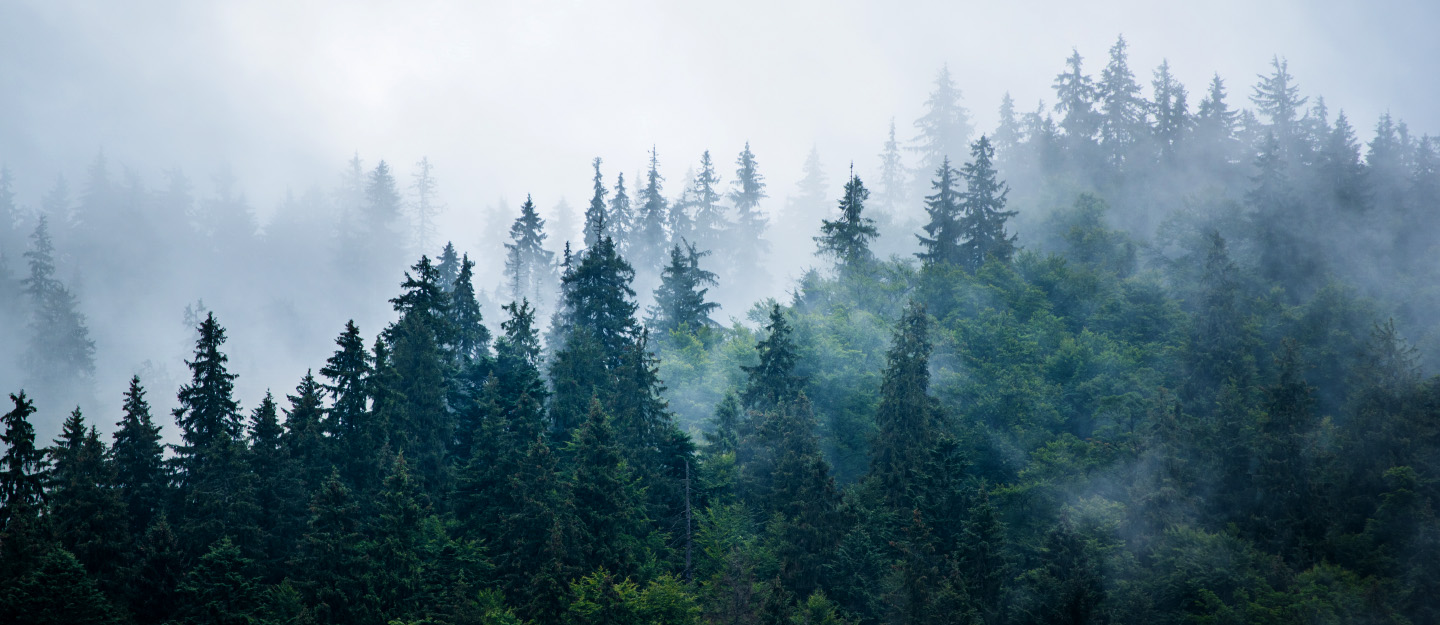
Forests in Pakistan play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance, supporting biodiversity, and providing resources for local communities. Covering about 5% of the country's total land area, these forests range from the dense coniferous forests of the northern mountains to the dry tropical forests in the south. They serve as vital habitats for diverse wildlife, help regulate the climate, and contribute to water conservation. However, deforestation, urbanization, and climate change pose significant threats to Pakistan’s forested areas. Conservation efforts and reforestation initiatives are essential to protect and restore these valuable natural resources.

Importance of Forests in Pakistan
Forests in Pakistan are of immense importance due to their environmental, economic, and social benefits. They act as natural carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide and helping combat climate change. Forests also prevent soil erosion, regulate water cycles, and reduce the risk of floods, especially in mountainous regions. Economically, they provide timber, fuelwood, and non-timber forest products that support livelihoods. Additionally, forests serve as habitats for diverse wildlife, contributing to biodiversity conservation. They also promote eco-tourism, offering scenic landscapes and recreational opportunities. Given the growing environmental challenges, sustainable forest management is crucial to ensure the long-term benefits of these valuable ecosystems.
Environmental Benefits
-
Climate Regulation: Absorb carbon dioxide and mitigate climate change effects.
-
Biodiversity Conservation: Provide habitat for wildlife.
-
Soil Protection: Prevent soil erosion and landslides.
-
Water Cycle Regulation: Maintain groundwater levels and prevent desertification.
Economic Benefits
-
Timber and Fuelwood Production: Source of raw material for industries.
-
Medicinal Plants: Used in pharmaceuticals.
-
Tourism and Recreation: Boosts eco-tourism in northern regions.
Social and Cultural Significance
-
Livelihood for Local Communities: Many indigenous people depend on forests.
-
Cultural and Religious Importance: Sacred groves in some regions.
Types of Forests in Pakistan
1. Alpine and Subalpine Forests
-
Location: Northern areas (Gilgit-Baltistan, Chitral, Swat).
-
Flora: Pine, fir, spruce.
-
Climate: Cold, high-altitude.
-
Importance: Prevents soil erosion and maintains biodiversity.
2. Coniferous Forests
-
Location: Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Azad Kashmir.
-
Flora: Deodar, blue pine, cedar.
-
Usage: Timber production.
3. Riverine (Riparian) Forests
-
Location: Along Indus River and its tributaries.
-
Flora: Acacia, shisham, babul.
-
Importance: Prevents floods and maintains water levels.
4. Tropical Thorn Forests
-
Location: Sindh, Punjab, Balochistan.
-
Flora: Kikar, keekar, wild olive.
-
Climate: Arid and semi-arid.
5. Mangrove Forests
-
Location: Coastal areas (Sindh, Balochistan).
-
Flora: Avicennia marina, Rhizophora.
-
Importance: Protects against coastal erosion, supports marine life.
6. Scrub Forests
-
Location: Pothohar Plateau, Salt Range.
-
Flora: Phulai, sanatha.
-
Usage: Grazing and firewood collection.
Challenges Facing Pakistan’s Forests
Pakistan’s forests face numerous challenges that threaten their sustainability and ecological balance. Rapid deforestation, primarily due to illegal logging, urban expansion, and agricultural encroachment, has significantly reduced forest cover. Climate change further exacerbates the situation by altering rainfall patterns and increasing the frequency of extreme weather events such as floods and droughts. Overgrazing by livestock and unsustainable fuelwood collection also contribute to forest degradation. Additionally, weak enforcement of conservation laws and lack of awareness about the importance of forests hinder effective management efforts. Addressing these challenges requires strong policy measures, afforestation initiatives, and community engagement to ensure the protection and restoration of Pakistan’s forests.
1. Deforestation
-
Rapid urbanization and agricultural expansion.
-
Illegal logging and timber mafia activities.
2. Climate Change
-
Rising temperatures and shifting rainfall patterns.
-
Increased risk of wildfires and desertification.
3. Overgrazing
-
Excessive livestock grazing leads to habitat destruction.
-
Loss of plant species due to trampling.
4. Water Scarcity
-
Droughts and reduced river flow affect riverine and mangrove forests.

Conservation Efforts in Pakistan
Pakistan has undertaken several conservation efforts to protect and restore its forests, recognizing their critical role in environmental sustainability. The government has launched large-scale afforestation projects such as the Billion Tree Tsunami in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and the Ten Billion Tree Tsunami Program nationwide to combat deforestation and increase green cover. Protected areas, including national parks and wildlife reserves, have been established to safeguard biodiversity. Additionally, laws and policies such as the Pakistan Forest Act aim to regulate logging and promote sustainable forest management. Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and local communities are also actively involved in tree plantation drives and awareness campaigns. Despite these efforts, challenges like illegal logging and climate change persist, highlighting the need for stricter enforcement and long-term conservation strategies.
1. Billion Tree Tsunami Project
-
Launched in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa in 2014.
-
Planted over one billion trees.
-
Recognized by international organizations.
2. 10 Billion Tree Tsunami Program
-
Nationwide afforestation initiative.
-
Aims to restore degraded forests and improve biodiversity.
3. Protected Areas Expansion
-
Establishment of new national parks.
-
Conservation of endangered species and ecosystems.
4. Community-Based Forestry
-
Engaging local communities in forest management.
-
Providing alternative livelihoods to reduce dependency on wood.
5. Legislation and Policies
-
Strengthening laws against illegal logging.
-
Promotion of sustainable forestry practices.
Comparative Table: Forest Types and Their Characteristics
|
Forest Type |
Location |
Key Species |
Importance |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Alpine & Subalpine |
Northern Pakistan |
Pine, Spruce, Fir |
Prevents erosion |
|
Coniferous |
KPK, Azad Kashmir |
Deodar, Cedar |
Timber production |
|
Riverine |
Indus River Basin |
Acacia, Shisham |
Flood prevention |
|
Tropical Thorn |
Sindh, Punjab, Balochistan |
Kikar, Wild Olive |
Arid zone greenery |
|
Mangrove |
Coastal Areas |
Avicennia, Rhizophora |
Coastal protection |
|
Scrub |
Pothohar, Salt Range |
Phulai, Sanatha |
Grazing land |
Forests in Pakistan are vital for environmental sustainability, economic stability, and biodiversity conservation. Despite facing deforestation and climate change threats, initiatives like afforestation programs, protected area expansions, and community-based conservation efforts are showing positive results. However, continued policy implementation and community involvement are essential to safeguard Pakistan’s green cover for future generations.




.gif)














Sign in
to continue to ilmkidunya.com