Global warming is one of the most critical challenges facing humanity today. It refers to the long-term increase in Earth's average temperature due to human activities, primarily the burning of fossil fuels. The consequences of this phenomenon are far-reaching, impacting ecosystems, economies, and human societies worldwide.
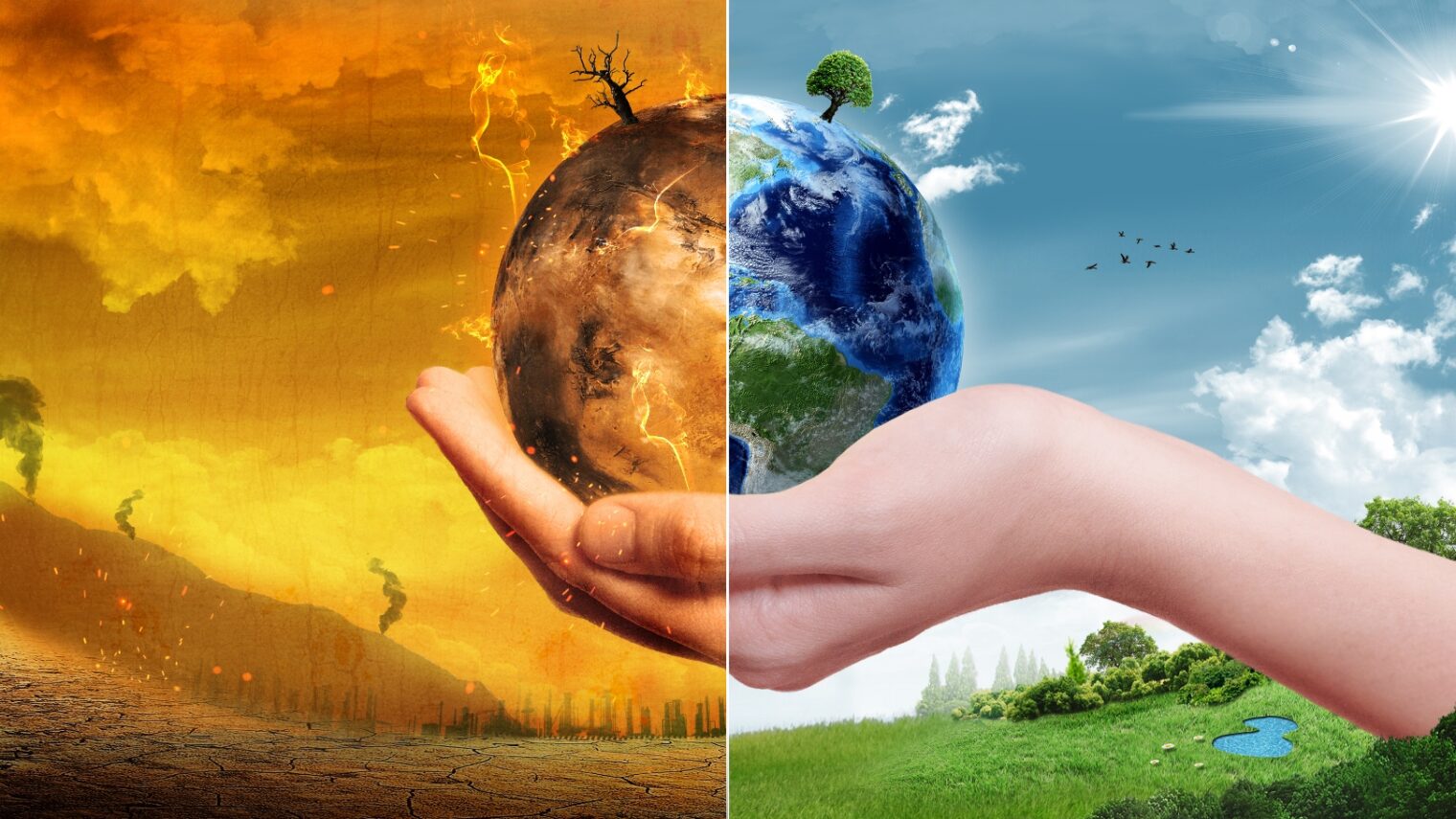

1. Rising Global Temperatures
One of the most direct effects of global warming is the continuous rise in global temperatures. According to NASA, the Earth's surface temperature has increased by approximately 1.2°C (2.2°F) since the late 19th century.
Temperature Rise Trends
Since the 1880s, global temperatures have shown a steady increase, with significant rises in the late 20th and early 21st centuries. Scientists link this trend to human-induced carbon emissions and deforestation, which have drastically altered the Earth's climate balance.
Rising temperatures have led to prolonged heatwaves, affecting not only human populations but also wildlife and vegetation. Extreme heat can cause droughts, putting stress on water resources and agricultural productivity. As temperatures continue to rise, regions that were once mild are experiencing record-breaking heat, causing widespread disruption to daily life. In some parts of the world, heatwaves are becoming more frequent and severe, leading to loss of life and increased demand for energy consumption due to air conditioning and cooling systems.
2. Melting Ice Caps and Rising Sea Levels
Global warming is causing glaciers and ice caps to melt at an alarming rate, leading to rising sea levels. This threatens coastal communities and small island nations
Effects of Melting Ice Caps:
-
Increased flooding in coastal cities
-
Loss of habitat for polar bears and other Arctic species
-
Higher risk of extreme weather events
Sea levels have risen significantly over the last century, affecting major coastal regions. Many areas are experiencing increased flooding and erosion, threatening both natural and human-built environments. Major cities like New York, London, and Mumbai are at risk of submersion if sea levels continue to rise at the current rate.
Furthermore, melting permafrost in Arctic regions is releasing methane, a potent greenhouse gas that exacerbates global warming. The loss of ice also means reduced reflectivity of sunlight, which in turn accelerates heating in polar regions, creating a dangerous feedback loop. This leads to further disruptions in the global climate system, affecting everything from ocean currents to monsoon patterns.
3. More Frequent and Intense Extreme Weather Events
Global warming is increasing the frequency and severity of extreme weather events, including hurricanes, wildfires, and heatwaves.
Key Consequences:
-
Hurricanes: Warmer ocean temperatures fuel stronger storms
-
Wildfires: Drought conditions increase fire outbreaks
-
Heatwaves: Higher temperatures cause deadly heatwaves, especially in urban areas
In addition, extreme rainfall events are becoming more common, leading to devastating floods and landslides. Many regions are experiencing unpredictable weather patterns, making it difficult for farmers to plan and maintain stable crop yields. These changes in weather patterns pose a serious threat to food security worldwide.
In some areas, hurricanes and typhoons are now stronger and more destructive due to the increased energy in the atmosphere. This has resulted in greater damage to homes, infrastructure, and livelihoods, displacing millions of people every year. Wildfires have become more frequent, destroying vast areas of forests and releasing large amounts of carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere, further accelerating climate change.
4. Impact on Biodiversity and Ecosystems
Climate change disrupts natural ecosystems, leading to biodiversity loss. Many species are struggling to adapt to rapid environmental changes.
Examples of Affected Species:
-
Polar Bears: Losing ice habitat in the Arctic
-
Coral Reefs: Bleaching due to rising ocean temperatures
-
Birds and Insects: Changing migration patterns due to shifting seasons
Ecosystem Disruptions:
-
Reduced agricultural yields due to unpredictable rainfall
-
Desertification of once-fertile lands
-
Loss of forests due to drought and fires
Forests, which play a critical role in carbon sequestration, are being lost at alarming rates due to wildfires and deforestation. The destruction of these ecosystems not only contributes to greenhouse gas emissions but also disrupts the delicate balance of biodiversity. Marine ecosystems are also under threat, as rising ocean temperatures and acidification harm fish populations, coral reefs, and aquatic plant life.
Additionally, changing climate conditions are affecting insect populations, which play a vital role in pollination and food production. The decline of pollinators such as bees and butterflies could have severe consequences for global agriculture and food security.
5. Economic and Social Consequences
The effects of global warming extend beyond environmental changes and significantly impact economies and human societies.
Economic Impacts:
Climate change negatively affects industries such as agriculture, fisheries, tourism, and infrastructure. Reduced crop yields, declining fish populations, and damage to natural attractions lead to economic downturns in many regions. Rising costs related to disaster recovery and adaptation measures also place an economic strain on communities and governments worldwide.
Extreme weather events cause billions of dollars in damages each year, straining national economies and displacing vulnerable populations. Countries that rely heavily on tourism, such as island nations, are experiencing significant economic losses as rising sea levels and coral bleaching diminish their natural attractions.
Social Consequences:
-
Increased displacement of people due to rising sea levels (climate refugees)
-
Higher risks of food and water scarcity
-
Increased health issues such as heat-related illnesses and the spread of vector-borne diseases
Climate-related migration is becoming an increasing concern as more people are forced to leave their homes due to environmental disasters. This leads to overcrowding in urban areas and places additional stress on social services, exacerbating poverty and inequality. In some cases, entire communities have been displaced due to rising waters, leading to loss of cultural heritage and traditional ways of life.
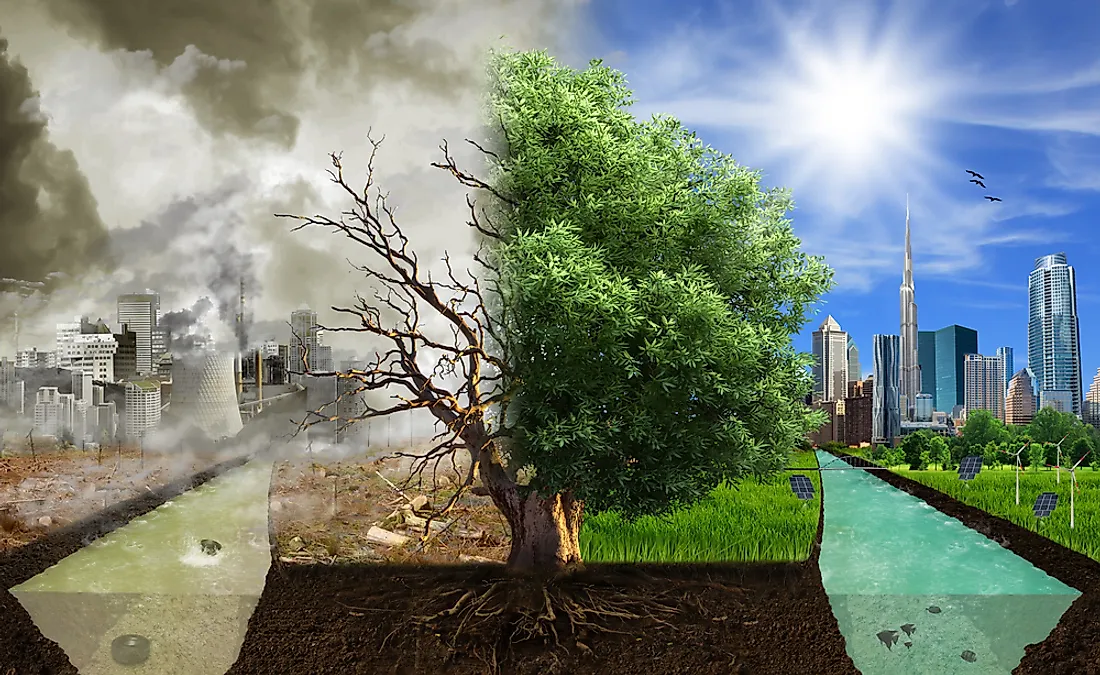

6. Solutions and Mitigation Strategies
To mitigate the effects of global warming, immediate action is necessary at individual, community, and governmental levels.
Strategies to Combat Climate Change:
-
Reducing Carbon Emissions: Shift to renewable energy sources like wind, solar, and hydropower.
-
Afforestation and Reforestation: Plant more trees to absorb CO2.
-
Energy Efficiency: Promote energy-saving technologies in industries and households.
-
Sustainable Agriculture: Implement eco-friendly farming techniques to reduce methane emissions.
-
Climate Policy and International Agreements: Support global initiatives like the Paris Agreement.
Encouraging sustainable urban planning and green infrastructure can help cities reduce their carbon footprint. Governments must invest in public transportation, energy-efficient buildings, and waste management systems to create more sustainable urban environments.




.gif)














Sign in
to continue to ilmkidunya.com