When purchasing a new display, whether for a TV, monitor, or mobile screen, the debate between LED and LCD is crucial. Many people assume they are entirely different technologies, but in reality, LED is a type of LCD. However, their differences in backlighting technology, power efficiency, and display performance can significantly impact your viewing experience.
Understanding these differences is essential, as they directly affect aspects like color accuracy, contrast levels, and overall display longevity. This guide will help you make an informed decision based on your needs.

1. What is an LCD?
Definition
An LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) is a flat-panel display technology commonly used in televisions, computer monitors, smartphones, and other electronic devices. It operates by using liquid crystals that do not emit light directly but instead manipulate light from a backlight to create images. The display consists of multiple layers, including polarized glass panels, a liquid crystal layer, color filters, and a backlight source, usually LED. When an electric current is applied, the liquid crystals align to control light passage, producing different colors and images. LCDs are known for their energy efficiency, thin design, and ability to provide clear and vibrant visuals.
How It Works
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) works by manipulating liquid crystals to control the passage of light and create images. It consists of multiple layers, including a backlight, polarizing filters, and liquid crystal molecules sandwiched between two glass panels. When an electric current passes through the liquid crystals, they align in a way that either blocks or allows light to pass through specific areas. This controlled light, combined with color filters, forms the pixels that make up an image. Since LCDs rely on a constant backlight, they are energy-efficient and produce clear, sharp visuals, making them widely used in televisions, monitors, and mobile devices.
The display consists of multiple layers, including a polarizing filter, liquid crystal layer, and color filter. When an electric current passes through the liquid crystals, they align to allow specific amounts of light through, creating the image.
Advantages
-
Energy-efficient compared to older CRT screens – LCDs consume significantly less power than bulky cathode-ray tube (CRT) displays.
-
Lightweight and thin – Unlike older display technologies, LCDs offer a sleeker, more modern design.
-
Better color accuracy compared to CRTs – The ability to filter colors results in sharper and more vibrant images.
-
No screen burn-in issues – Unlike OLED screens, LCDs do not suffer from permanent image retention.
Disadvantages
-
Black levels are not true black – Due to backlighting, LCDs struggle to produce deep blacks.
-
Slower response time compared to LEDs – This can lead to ghosting in fast-moving images.
-
Limited viewing angles – Colors and contrast degrade when viewed from an angle.
2. What is an LED?
Definition
An LED (Light Emitting Diode) is a semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current passes through it. It works based on the principle of electroluminescence, where electrons recombine with holes in the semiconductor material, releasing energy in the form of photons (light). LEDs are widely used for lighting, display screens, indicators, and electronic devices due to their energy efficiency, long lifespan, and durability. Unlike traditional incandescent bulbs, LEDs do not rely on a filament, which makes them more efficient and less prone to failure. They are available in various colors and can be combined to produce different lighting effects and high-quality digital displays.
How It Works
LED (Light Emitting Diode) works by passing an electric current through a semiconductor material, which then emits light through a process called electroluminescence. The LED consists of a positive (p-type) and a negative (n-type) semiconductor junction. When voltage is applied, electrons from the n-type region combine with holes from the p-type region, releasing energy in the form of photons (light). The color of the light depends on the semiconductor material used. LEDs are highly energy-efficient, long-lasting, and generate less heat compared to traditional bulbs, making them ideal for displays, lighting, and electronic indicators.
-
Edge-Lit LED: LEDs are placed around the edges of the display, directing light toward the center.
-
Direct-Lit LED: LEDs are spread behind the screen, offering uniform brightness.
-
Full-Array LED: LEDs cover the entire back panel, allowing for precise brightness control and better contrast.
Advantages
-
More energy-efficient than CCFL-based LCDs – LED technology consumes less power while delivering better brightness.
-
Better contrast and deeper blacks – With localized dimming, LED displays achieve darker blacks.
-
Improved brightness and sharper images – Ideal for outdoor visibility and bright environments.
-
Thinner and lighter design – LED technology allows for ultra-slim screens.
-
Longer lifespan – LEDs have a longer operational life compared to CCFLs.
Disadvantages
-
More expensive than traditional LCDs – The additional benefits come at a higher price point.
-
Color accuracy may vary between models – Some LED displays may struggle with color consistency.
-
Edge-lit models may have uneven brightness – Some areas may appear brighter than others.
3. Key Differences Between LED and LCD
The following table summarizes the main differences between LED and LCD displays:
|
Feature |
LCD (CCFL Backlit) |
LED (LED Backlit) |
|---|---|---|
|
Backlighting |
CCFL (Fluorescent) |
LED (Light Emitting Diode) |
|
Energy Efficiency |
Higher power consumption |
Lower power consumption |
|
Black Levels |
Less deep blacks |
Better black levels |
|
Brightness |
Standard |
Higher brightness |
|
Thickness |
Thicker |
Thinner |
|
Color Accuracy |
Good |
Better |
|
Lifespan |
Shorter |
Longer |
|
Cost |
Generally cheaper |
More expensive |
|
Viewing Angles |
Narrower |
Wider |
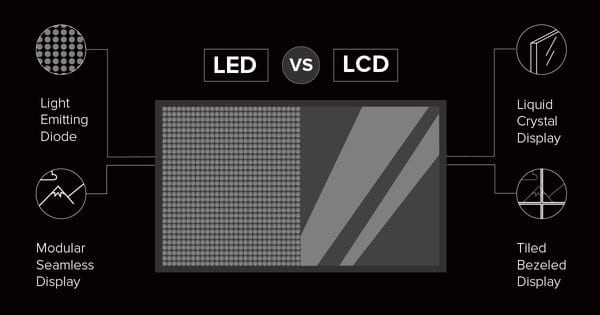
4. Which One is Better for You?
Choose LED If:
If you are looking for a high-quality display with excellent brightness, energy efficiency, and deep contrast, LED is the better option. It is particularly ideal for gamers, home theaters, and anyone who values sharp image quality.
✔️ You want better energy efficiency. LEDs consume less power, making them a more eco-friendly choice.
✔️ You prefer higher brightness and contrast. Ideal for watching movies and playing games in high-definition.
✔️ You want a thinner and more stylish screen. LED displays are sleek and modern.
✔️ You are looking for a longer-lasting display. LEDs outlast CCFL-based LCDs.
Choose LCD If:
For those who are on a tight budget and do not require extreme contrast or brightness, LCDs are still a viable choice. They work well for basic office tasks, casual gaming, and standard TV viewing.
✔️ You are on a budget. LCDs are generally cheaper than LED models.
✔️ You don’t need extreme brightness or contrast. If you use your screen in a dimly lit room, an LCD can suffice.
✔️ You are okay with a slightly thicker display. Thickness is not an issue for many users.
While both LED and LCD displays use liquid crystal technology, LED displays are superior due to their better brightness, energy efficiency, contrast, and lifespan. However, if affordability is your main concern, LCDs still provide a decent viewing experience.
Before making a purchase, carefully assess factors such as your budget, usage requirements, and preferred display quality. Whether you're looking for a screen for gaming, work, or entertainment, choosing the right display will enhance your overall experience.




.gif)














Sign in
to continue to ilmkidunya.com