Face recognition is a biometric technology that identifies or verifies an individual based on facial features. It captures, analyzes, and compares patterns from images or video footage. The system uses advanced AI and ML algorithms to enhance accuracy and efficiency.
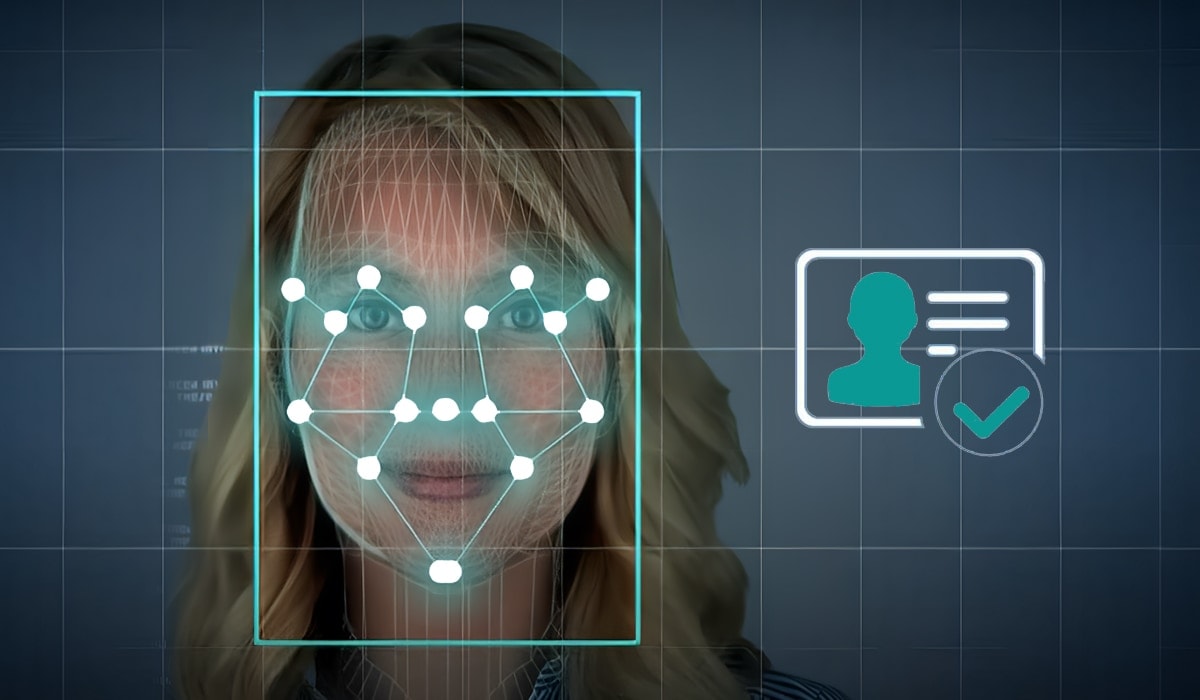
How Face Recognition Works
Face recognition technology follows a structured process that involves multiple steps. Below are the key steps in facial recognition:
1. Face Detection
The first step is detecting the presence of a face in an image or video. Face detection technology identifies and locates human faces using deep learning models. The two common techniques used are:
-
Haar Cascade Classifier: A traditional computer vision approach for face detection.
-
Deep Learning-based Methods: Such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), which offer higher accuracy.
2. Face Alignment
Once a face is detected, the system aligns it to ensure proper positioning for accurate recognition. The alignment process includes:
-
Normalizing the image to match standard dimensions.
-
Adjusting facial angles to correct distortions.
-
Detecting key facial landmarks like eyes, nose, and mouth for proper alignment.
3. Feature Extraction
Feature extraction is the process of identifying unique facial characteristics, such as:
-
Eye shape and distance
-
Nose structure
-
Jawline contours
-
Skin texture and patterns
Deep learning models extract these features to create a unique facial representation.
4. Face Encoding
The extracted features are converted into numerical data, known as facial embeddings. This numerical representation allows the system to compare faces efficiently.
5. Face Matching and Verification
Once a face is encoded, it is compared against a database for identification or authentication. This process includes:
-
1:1 Matching (Verification): Comparing a captured face with a stored image (e.g., unlocking a phone with Face ID).
-
1:N Matching (Identification): Comparing a face against a large database to find the best match (e.g., identifying a suspect in law enforcement systems).
6. Decision Making
The system then determines whether the captured face matches any stored records. If a match is found, the identity is verified; otherwise, access is denied or flagged.
Applications of Face Recognition
Face recognition technology is used across various industries for different purposes. Some key applications include:
Security and Surveillance
-
Law enforcement agencies use facial recognition to track criminals.
-
Airports employ the technology for passport verification.
-
Public surveillance systems enhance safety in crowded places.
Personal Authentication
-
Smartphone unlocking with Face ID.
-
Biometric authentication in banking and finance.
-
Access control in corporate environments.
Retail and Marketing
-
Customer identification for personalized shopping experiences.
-
Analyzing customer behavior and demographics for targeted advertising.
Healthcare
-
Patient identification in hospitals.
-
Monitoring patient health conditions.
Social Media and Entertainment
-
Auto-tagging in photos on social media platforms.
-
Augmented reality (AR) filters and effects.
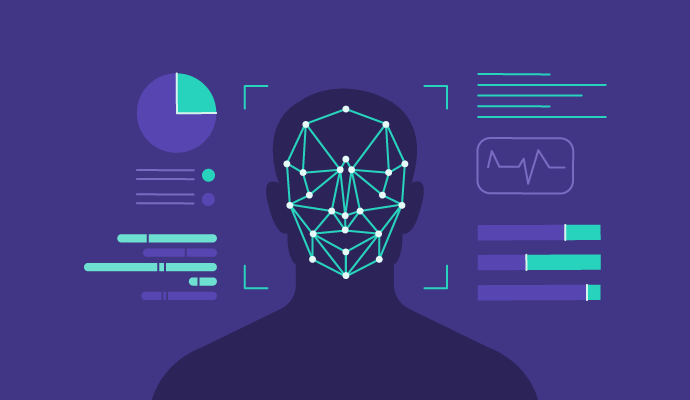

Advantages of Face Recognition Technology
Face recognition offers several benefits over traditional security methods:
-
High Accuracy: Advanced AI models provide precise identification.
-
Convenience: Eliminates the need for passwords or ID cards.
-
Fast and Efficient: Provides real-time authentication and access.
-
Enhanced Security: Prevents unauthorized access and identity fraud.
-
Non-Intrusive: Does not require physical contact like fingerprint scanning.
Challenges and Concerns
Despite its advantages, facial recognition technology faces certain challenges and concerns:
Privacy Issues
-
Unauthorized use of personal data.
-
Lack of user consent in public surveillance.
Accuracy and Bias
-
Racial and gender biases in facial recognition algorithms.
-
Errors in recognition leading to false matches.
Security Risks
-
Vulnerability to spoofing attacks (e.g., using photos or deepfake videos to bypass authentication).
-
Data breaches compromising facial data storage.
Ethical Concerns
-
Potential misuse in mass surveillance.
-
Ethical dilemmas in government and corporate use.
Future of Face Recognition
With rapid advancements in AI and deep learning, face recognition technology is continuously evolving. Some emerging trends include:
-
3D Face Recognition: Enhanced depth sensing for improved accuracy.
-
AI-powered Anti-Spoofing: Better detection of fake faces and deepfakes.
-
Edge AI Processing: On-device facial recognition for increased privacy.
-
Blockchain-based Security: Secure facial data storage to prevent hacking.
Face recognition technology has revolutionized security, authentication, and convenience across various industries. While it offers numerous benefits, it also raises privacy and ethical concerns that need to be addressed. With ongoing advancements, the future of face recognition promises improved accuracy, security, and responsible usage.




.gif)















Sign in
to continue to ilmkidunya.com