Dams play a crucial role in Pakistan's water management, energy production, and agriculture. With a growing population and increasing demand for water and electricity, Pakistan has investedsignificantly in dam construction. This article explores major dams in Pakistan, their benefits, challenges, and future projects.
Importance of Dams in Pakistan
Dams are essential for various sectors, including agriculture, energy, and flood control. Some key benefits include:
-
Water Storage: Ensuring a steady supply of water for domestic and industrial use.
-
Irrigation Support: Helping agriculture by providing consistent water flow.
-
Hydropower Generation: Reducing dependence on fossil fuels and generating clean energy.
-
Flood Control: Managing seasonal floods and minimizing damage to infrastructure.
-
Recreational and Fisheries Development: Supporting tourism and fishing industries.

Major Dams in Pakistan
Pakistan has several major dams, categorized based on their purposes such as hydropower generation, irrigation, and water storage. Below is a table highlighting key dams:
Table: Major Dams in Pakistan
|
Dam Name |
Location |
River |
Type |
Storage Capacity (MAF) |
Power Generation (MW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Tarbela Dam |
Khyber Pakhtunkhwa |
Indus |
Earth-fill |
13.69 |
4,888 |
|
Mangla Dam |
Azad Kashmir |
Jhelum |
Concrete |
7.4 |
1,310 |
|
Diamer-Bhasha Dam |
Gilgit-Baltistan |
Indus |
RCC |
8.1 |
4,500 (planned) |
|
Mohmand Dam |
Khyber Pakhtunkhwa |
Swat |
RCC |
1.2 |
800 (planned) |
|
Dasu Dam |
Khyber Pakhtunkhwa |
Indus |
RCC |
N/A |
4,320 (planned) |
|
Neelum-Jhelum Dam |
Azad Kashmir |
Neelum |
Concrete |
N/A |
969 |
Tarbela Dam
Tarbela Dam, located on the Indus River in Pakistan, is one of the largest earth-filled dams in the world. Completed in 1976, it was built to regulate water flow for irrigation, hydroelectric power generation, and flood control. The dam plays a crucial role in Pakistan’s economy by supporting agriculture through its vast reservoir and providing a significant portion of the country’s electricity through its hydroelectric power stations, which have a current capacity of over 6,400 MW. Over the years, expansion projects have been undertaken to enhance its power generation and water storage capacity. Despite challenges such as sedimentation reducing its storage capacity, Tarbela Dam remains a vital infrastructure project for Pakistan’s water and energy needs.
Features
-
Located on the Indus River.
-
Commissioned in 1976.
-
Generates 4,888 MW of electricity.
-
Provides irrigation water to millions of acres of farmland.
Mangla Dam
Mangla Dam, located on the Jhelum River in Pakistan, is the second-largest water reservoir in the country after Tarbela Dam. Constructed in 1967 as part of the Indus Basin Project, it was designed to store water for irrigation and generate hydroelectric power. The dam stands 147 meters (482 feet) high and has a reservoir capacity of approximately 7.4 million acre-feet (MAF). Over the years, its power generation capacity has been expanded to 1,310 MW. Besides playing a crucial role in Pakistan’s agriculture and energy sectors, Mangla Dam also helps in flood control. To counteract sedimentation and increase storage capacity, the dam was raised by 30 feet in a major expansion project. It remains a key asset for Pakistan’s water management and power supply.
Features
-
Built on the Jhelum River.
-
Commissioned in 1967.
-
Produces 1,310 MW of electricity.
-
Acts as a major water reservoir for Punjab and Sindh.
Diamer-Bhasha Dam (Under Construction)
Diamer-Bhasha Dam, currently under construction on the Indus River in Pakistan, is set to become one of the largest dams in the country. Located in the Gilgit-Baltistan region, the dam is designed to store 8.1 million acre-feet (MAF) of water and generate 4,500 megawatts (MW) of hydroelectric power. Its primary objectives include water storage for irrigation, flood control, and reducing sedimentation in downstream reservoirs like Tarbela Dam. Once completed, it will significantly enhance Pakistan’s water and energy security, helping to meet growing agricultural and industrial demands. The project, launched in 2020, is expected to be completed in phases over the coming years, playing a crucial role in the country's long-term development.
Features
-
Located on the Indus River in Gilgit-Baltistan.
-
Expected completion by 2028.
-
Planned storage capacity of 8.1 MAF.
-
Projected 4,500 MW power generation.
Future Dams in Pakistan
Pakistan is actively working on constructing new dams to enhance water storage and energy production. Below are some upcoming projects:
Table: Upcoming Dams in Pakistan
|
Dam Name |
Location |
River |
Expected Completion |
Power Generation (MW) |
|
Dasu Dam |
Khyber Pakhtunkhwa |
Indus |
2028 |
4,320 |
|
Mohmand Dam |
Khyber Pakhtunkhwa |
Swat |
2027 |
800 |
|
Kalabagh Dam (Proposed) |
Punjab |
Indus |
TBD |
3,600 |
|
Bunji Dam |
Gilgit-Baltistan |
Indus |
TBD |
7,100 |
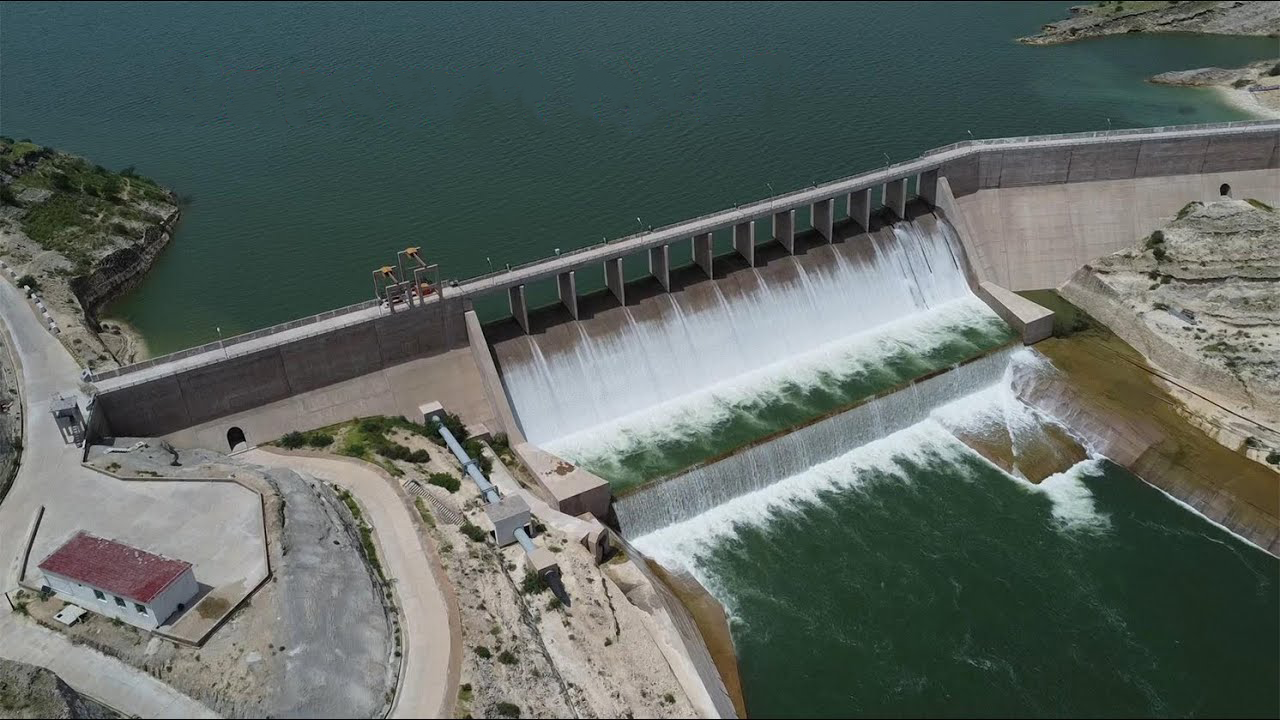

Challenges Facing Dam Construction in Pakistan
Despite the importance of dams, several challenges hinder their construction and maintenance:
-
High Costs: Large-scale dam projects require massive investment.
-
Environmental Impact: Dams can disrupt ecosystems and affect local wildlife.
-
Land Acquisition Issues: Displacement of communities leads to social resistance.
-
Sedimentation: Over time, silt accumulation reduces water storage capacity.
-
Climate Change: Altered rainfall patterns can impact dam efficiency.
Government Initiatives and Policies
The government has taken several measures to overcome these challenges and promote dam construction:
-
CPEC Collaboration: Joint projects with China to develop hydropower dams.
-
Public-Private Partnerships: Encouraging private sector investment.
-
International Funding: Seeking financial aid from World Bank and ADB.
-
Awareness Campaigns: Educating the public on the importance of water conservation.
Dams are vital for Pakistan’s water and energy security. While existing dams contribute significantly to the country's economy, future projects like Diamer-Bhasha and Mohmand Dam will further enhance capacity. Addressing challenges through sustainable policies and international collaboration will ensure long-term benefits for Pakistan’s development.




.gif)















Sign in
to continue to ilmkidunya.com